Liothyronine
CAS number: 6893-02-3
Liothyronine is a thyroidal hormone T3 which is normally produced by the thyroid gland in a ratio 4:1 when compared with T4: T3. Liothyronine is the active form of thyroxine which is composed in a basic chemical structure by a tyrosine with bound iodine. The exogenous liothyronine product was developed by King Pharmaceuticals and FDA approved in 1956.
Related images
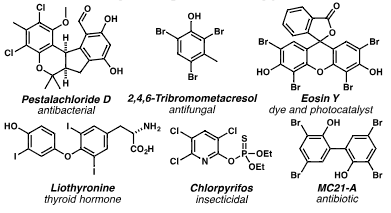
Selected haloarenes: Pestalachloride D, 2,4,6-Tribromo-m-cresol, Eosine Y, Liothyronine, Chlorpyrifos, mC21-A.
Related Questions and Answers
A: The study found that the Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) remained stable throughout the study. There were no significant changes in other clinical measures such as the Symbol Digit Modalities Test (SDMT), Multiple Sclerosis Functional Composite (MSFC), Functional Assessment of Multiple Sclerosis (FAMS), or Mood 24/7. However, a slight improvement in the timed 25-foot walk test (T25FW) was observed in progressive MS patients, and a trend for improved thinking/fatigue was noted in relapsing MS patients.
A: The most common adverse events reported during the study included gastrointestinal distress, fatigue, headaches, insomnia, and palpitations. These events were generally mild (Grade 1) and self-limiting. One participant experienced bowel incontinence and abdominal pain, which resolved after stopping the study drug. No severe or serious adverse events related to the study drug were reported.
A: The study observed changes in serum thyroid function tests, but these changes did not result in clinical thyrotoxicosis. Four out of the initial seven participants required dose reductions due to asymptomatic low TSH levels. After revising the dose escalation schedule, no further dose reductions were needed, and no participants experienced clinical thyrotoxicosis.
A: Liothyronine is being investigated for its potential to promote remyelination and neuroprotection in MS. The study found that liothyronine was well-tolerated and did not cause severe adverse events or disease activation in individuals with MS. It also showed potential biological effects within the central nervous system (CNS), particularly in proteins associated with immune function and angiogenesis.