Betaine
CAS number: 107-43-7
Betaine is a non-essential amino acid with proven functional properties and underutilized potential.
Related images
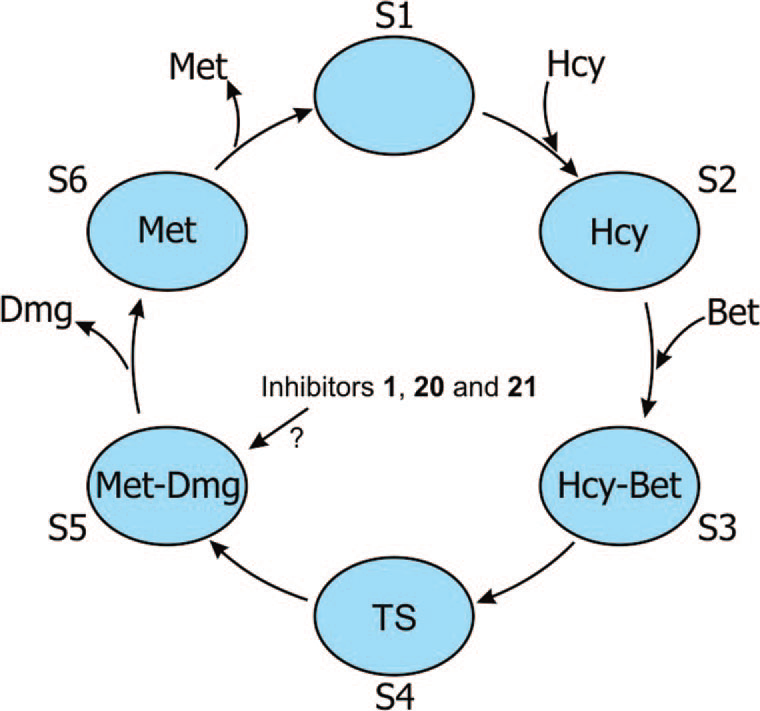
Schematic diagram showing the possible structural changes of BHMT during the binding process with substrates and products. The blue ovals (S1-S6) represent the different structural states of BMHT monomers. Hcy represents homocysteine, Bet represents betaine, Met represents methionine, Dmg represents dimethylglycine, and TS represents the assumed transition state of the substrate.
Related Questions and Answers
A: Dietary betaine significantly decreases hepatic triglycerides (TGs) content in laying hens. This reduction is associated with the suppression of sterol regulatory element binding transcription factor 1 (SREBP1), fatty acid synthase (FASN), and stearoyl-CoA desaturase (SCD) gene expression, and the activation of carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1A (CPT1A) gene expression. Furthermore, betaine supplementation leads to higher 5mC methylation levels on FASN and SCD gene promoters, lower 5mC methylation levels on CPT1A gene promoter, and an increased m6A methylation level on the 3' untranslated region of SREBP1 mRNA.