Fatty acids
CAS number: 67254-79-9
Fatty acids, one class of essential nutrients for humans, are an important source of energy and an essential component of cell membranes. Most fatty acids in plants and animals have an even carbon number and no branching. One or more double bonds may occur, mostly in cis configuration. More than 40 different fatty acids are commonly encountered in foods.
Related images
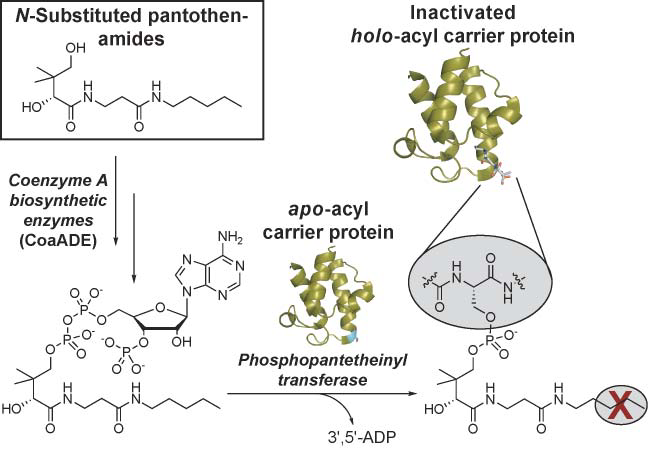
N-Substituted pantothenamides (such as N-pentyl pan- tothenamide shown above) act as antimetabolites by forming coenzyme A analogues which do not contain the essential terminal thiol group of natural CoA. These analogues subsequently transfer inactive prosthetic groups to the acyl carrier proteins that are involved in fatty acid metabolism, thereby blocking these processes.
Related Questions and Answers
A: Maternal dietary intake was assessed using 7-day food diaries analyzed with Spanish DIAL 1.0 software, quantifying myristic, palmitic, stearic, palmitoleic, oleic, linoleic, α-linolenic, arachidonic (ARA), eicosapentaenoic (EPA), and docosahexaenoic (DHA) acids.
A: Among others, the secreted protein P9 (binds ICAM-2 on L-cells), outer-membrane protein Amuc_1100, short-chain fatty acids (e.g., propionate via FFAR activation), and extracellular vesicles (AmEVs) have all been shown to stimulate GLP-1 release and improve glucose homeostasis.