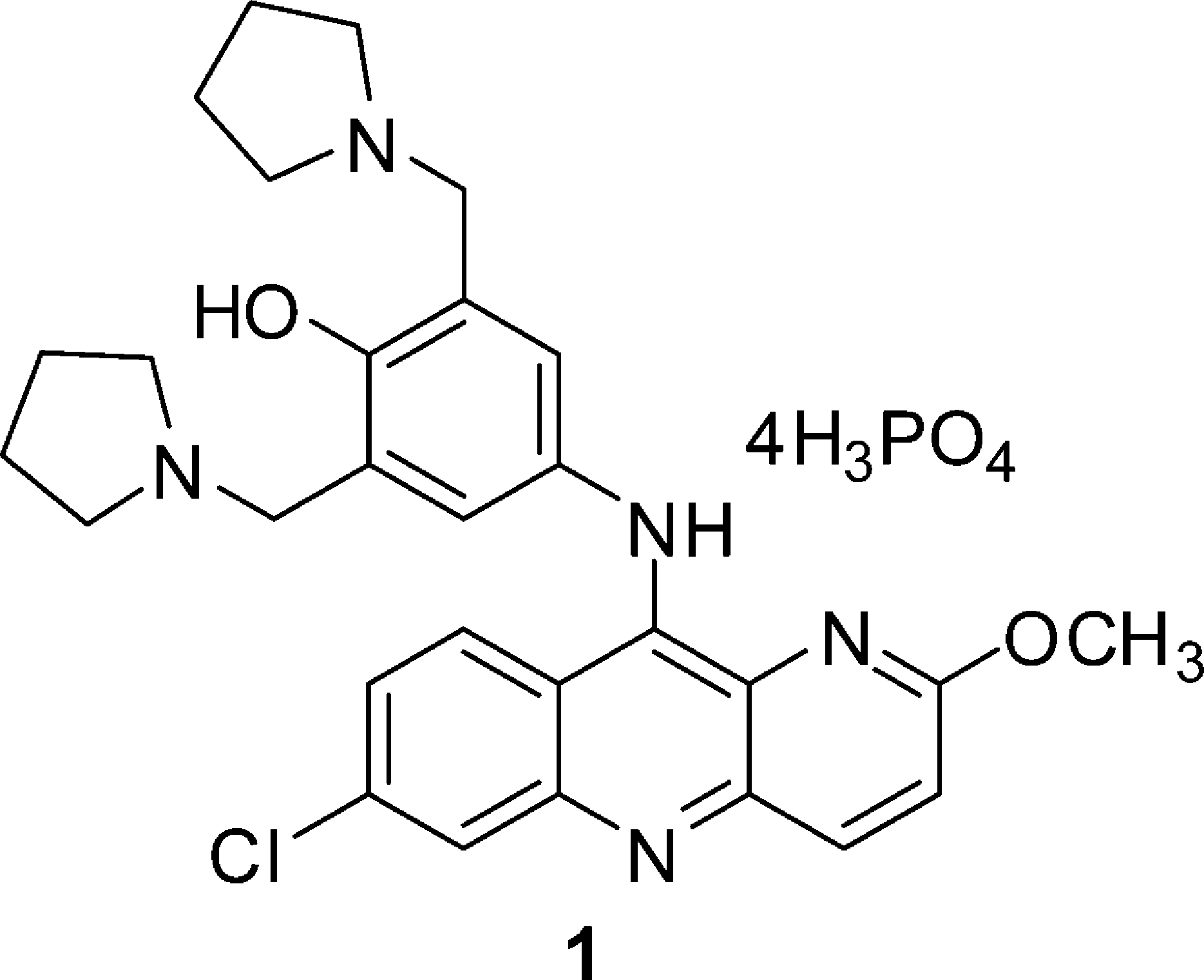
Pyronaridine tetraphosphate
CAS number: 76748-86-2
Pyronaridine tetraphosphate is a small molecule drug with a maximum clinical trial phase of II (across all indications) and has 4 investigational indications.
Related images
Related Questions and Answers
A: The mechanism of action of pyronaridine tetraphosphate involves inhibiting the papain-like protease (PLpro) of SARS-CoV-2 and other coronaviruses. By targeting this protease, pyronaridine disrupts the viral replication process, leading to reduced viral titers and improved disease outcomes. This inhibition of PLpro is effective across multiple coronaviruses due to the high conservation of this domain, making pyronaridine a promising broad-spectrum antiviral agent. Additionally, pyronaridine exhibits anti-inflammatory effects by reducing pro-inflammatory cytokine levels, further contributing to its therapeutic efficacy in treating coronavirus infections.
A: Pyronaridine tetraphosphate demonstrates comparable efficacy to molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir in reducing SARS-CoV-2 viral titers and lung pathology. In mouse models, pyronaridine achieved significant reductions in viral load and inflammatory markers similar to those observed with molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir. Additionally, combination treatments with pyronaridine and these antivirals showed additive effects, further reducing viral titers and inflammation. This suggests that pyronaridine could be a viable alternative or complementary treatment to existing antivirals, potentially offering broader-spectrum activity against multiple coronavirus variants.
A: Pyronaridine tetraphosphate acts as a potent antiviral and anti-inflammatory agent against highly pathogenic coronaviruses. It inhibits the viral PLpro, reducing viral replication and lung pathology. In mouse models, pyronaridine significantly lowered viral titers, reduced lung inflammation, and improved survival rates. It also showed additive effects when combined with other antivirals like molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir, further reducing viral loads and inflammatory markers. These findings suggest that pyronaridine could be a valuable therapeutic option for treating COVID-19 and other coronavirus infections, either as a standalone treatment or in combination with existing antivirals.