Ethanol
CAS number: 64-17-5
Ethanol, also known as ethyl alcohol or grain alcohol, is a clear, colorless liquid that is a type of alcohol. It's commonly used as a fuel, in alcoholic beverages, and in various industrial and medical applications.
Related images
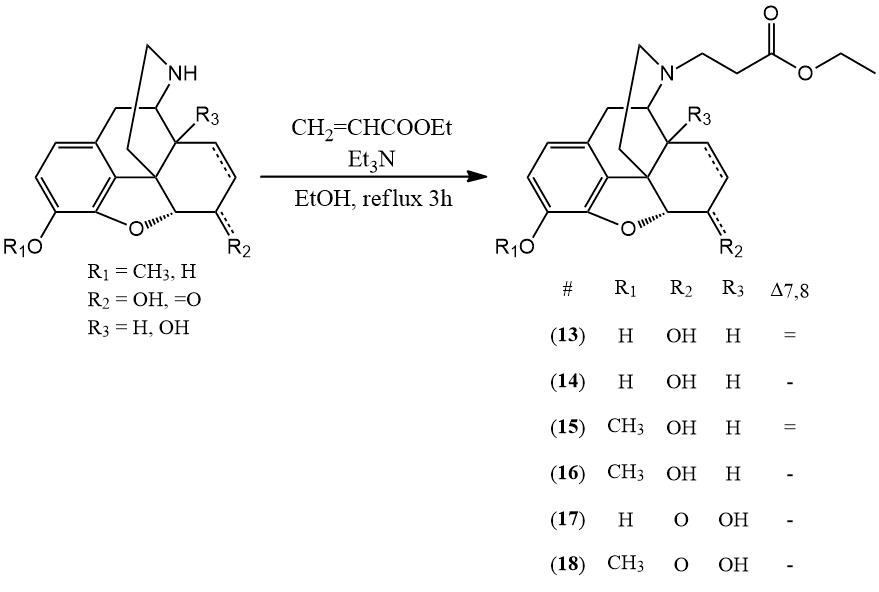
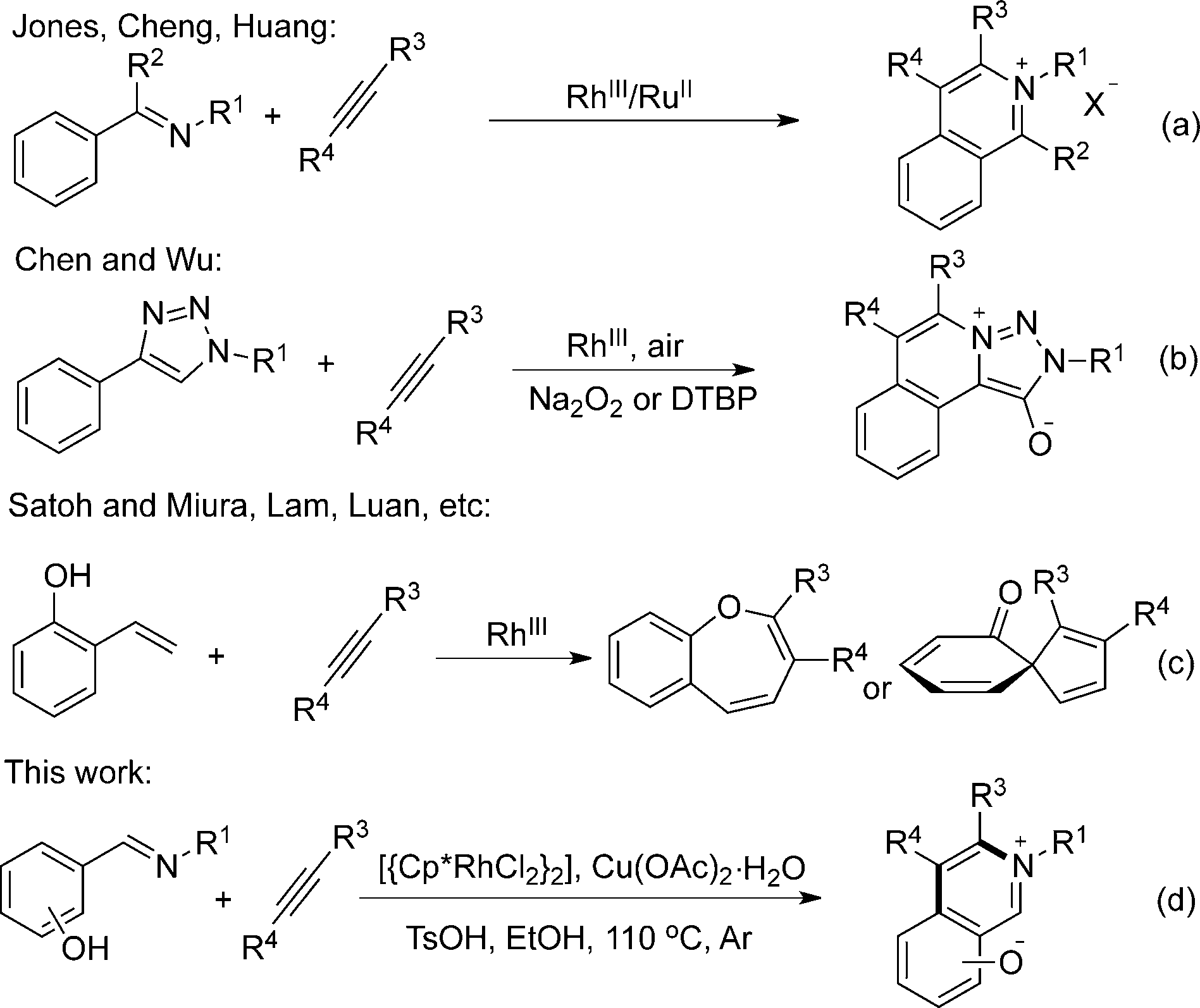
N-alkylation of nor-compounds: ethyl acrylate, triethylamine, ethanol, refl. 3 h.
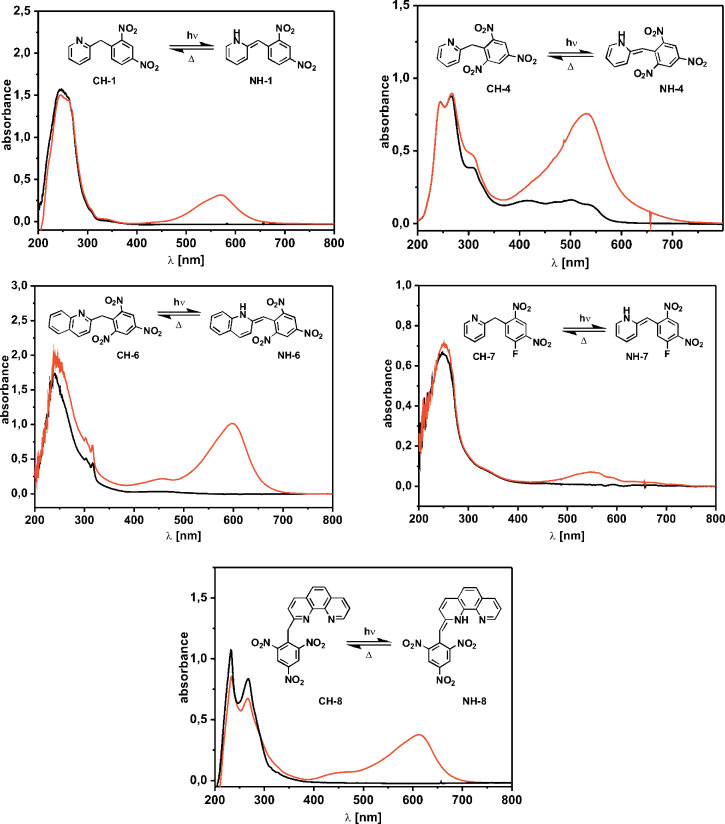
UV spectra of photoswitchable acids 1, 4, 6, 7, and 8 in ethanol in the CH form, before (black curve) and after irradiation, (red curve, formation of the NH form).
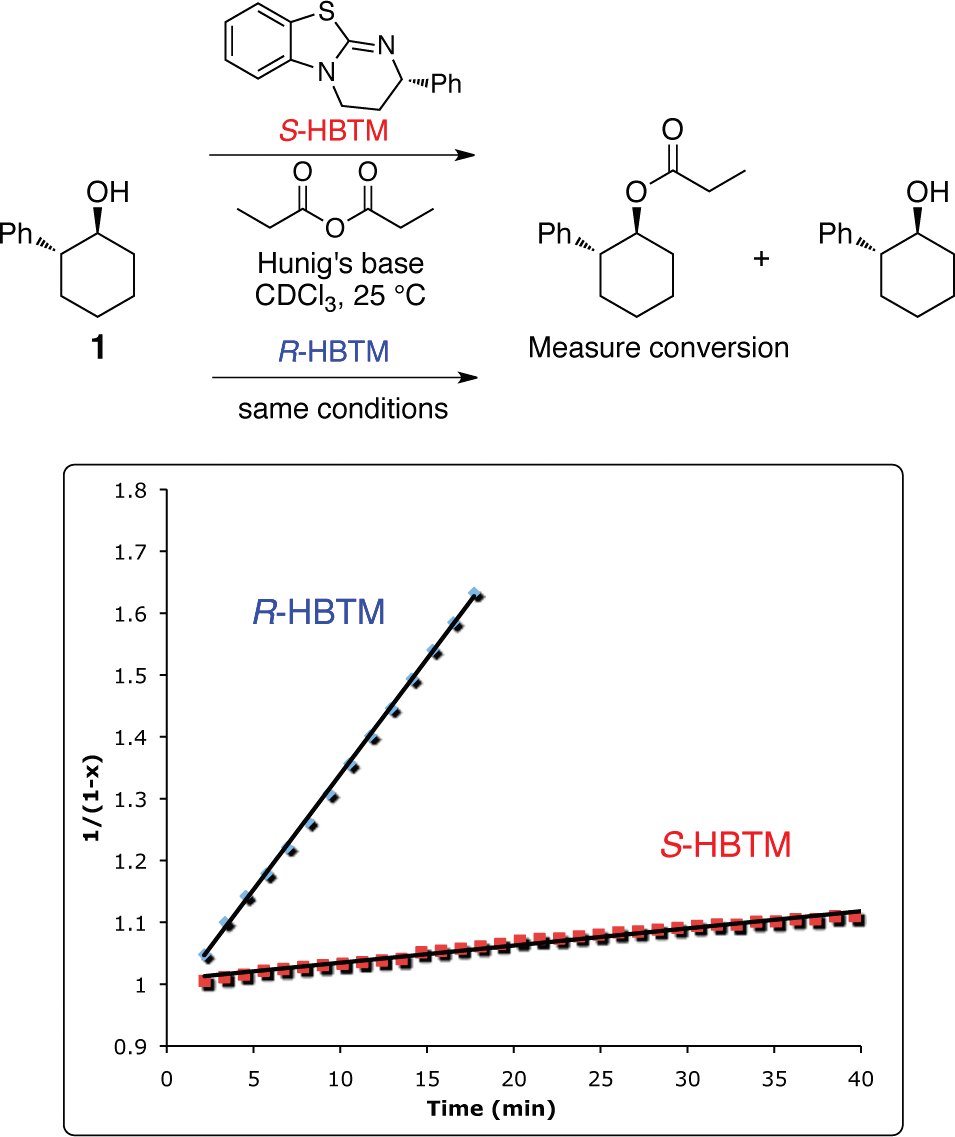
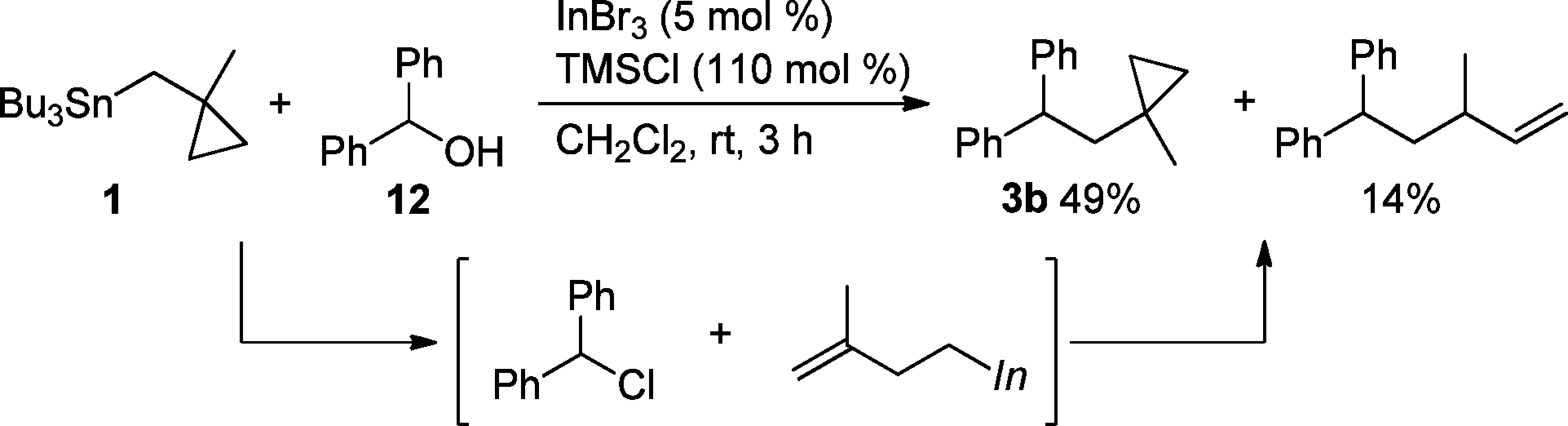
Optically pure alcohol 1 was reacted with propionic anhydride and either 5 mol % of S-HBTM or 5 mol % of R-HBTM catalyst.
Related Questions and Answers
A: Acetobacter ghanensis JN01 biodegrades ethanol by oxidizing it to acetaldehyde using alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH), and then converting acetaldehyde to acetate using aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH). The resulting acetate can be further converted to acetyl-CoA and fed into the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. This process prevents the accumulation of toxic acetaldehyde.
A: Ethanol serves as a green solvent for the electrochemical coupling reactions, providing a suitable medium for the reduction and dimerization of beta-nitrostyrene. It facilitates the proton transfer and stabilizes reactive intermediates, contributing to the high yield of the desired product.