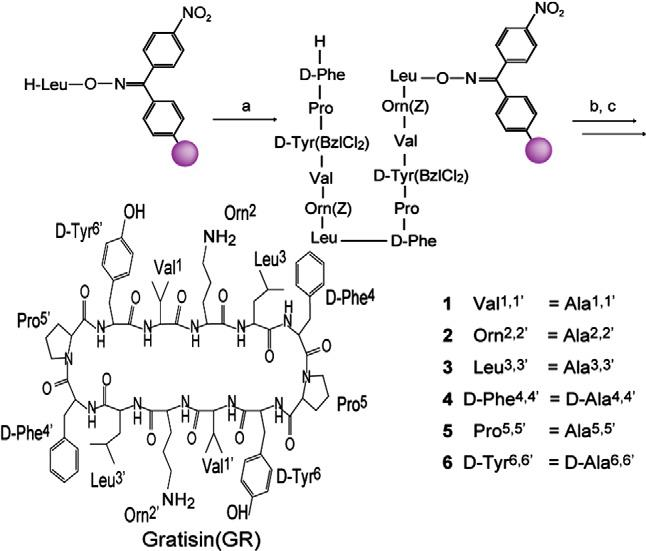
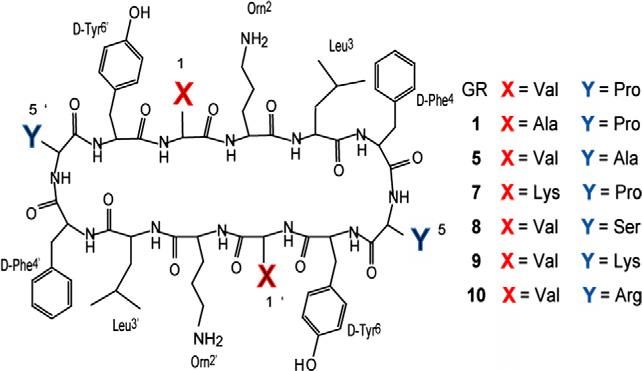
Gratisin
CAS number: 37294-30-7
Gratisin is a large, complex cyclic depsipeptide belongs to the class of synthetic macrocyclic peptidomimetics, engineered to mimic the structural and functional properties of natural peptides, often with improved stability and specificity. Gratisin features multiple chiral centers and functional groups, including amino, hydroxyl, isobutyl, isopropyl, and benzyl side chains, arranged in a highly stereospecific three-dimensional scaffold.
Related images
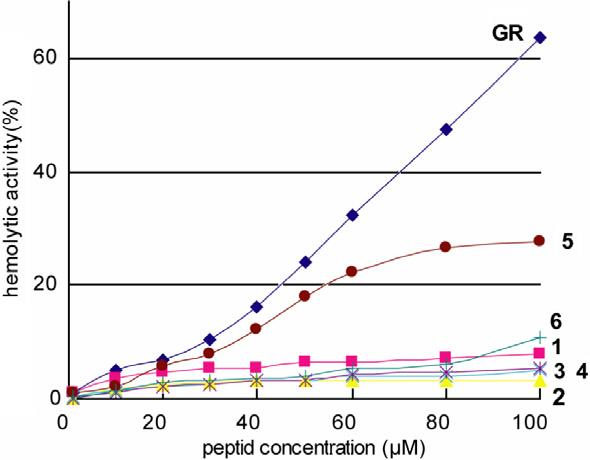
Dose dependence curves of hemolysis (%) induced by Gratisin and its Ala-substituted analogues 1–6.
Related Questions and Answers
No related questions yet