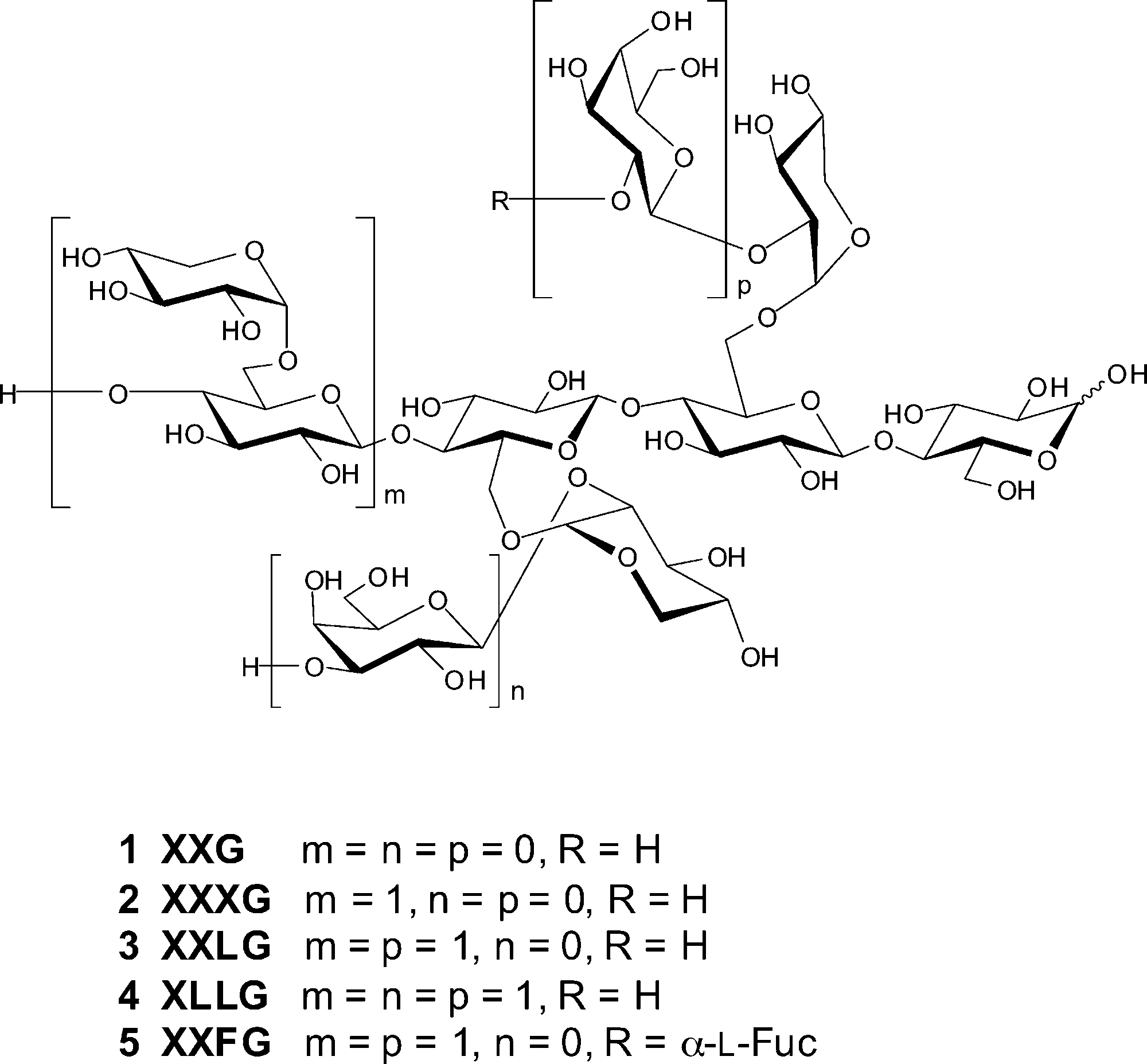
Xyloglucan
CAS number: 37294-28-3
Xyloglucan is a type of hemicellulose, a major component of plant cell walls, particularly in the primary cell wall. It's a polysaccharide made up of a backbone of (1->4)-linked β-D-glucan, with side chains of xylose, galactose, and sometimes fucose, attached to the backbone. Xyloglucan plays a crucial role in maintaining cell wall structure and is believed to be a key component in the network of cellulose and other polysaccharides that provides strength to plant cells.
Related images
Related Questions and Answers
No related questions yet