Cidofovir
CAS number: 113852-37-2
Cidofovir is an injectable antiviral medication employed in the treatment of cytomegalovirus (CMV) retinitis in patients diagnosed with AIDS. It suppresses CMV replication through selective inhibition of viral DNA synthesis. It was manufactured by Gilead and initially approved by the FDA in 1996, but has since been discontinued.
Related images
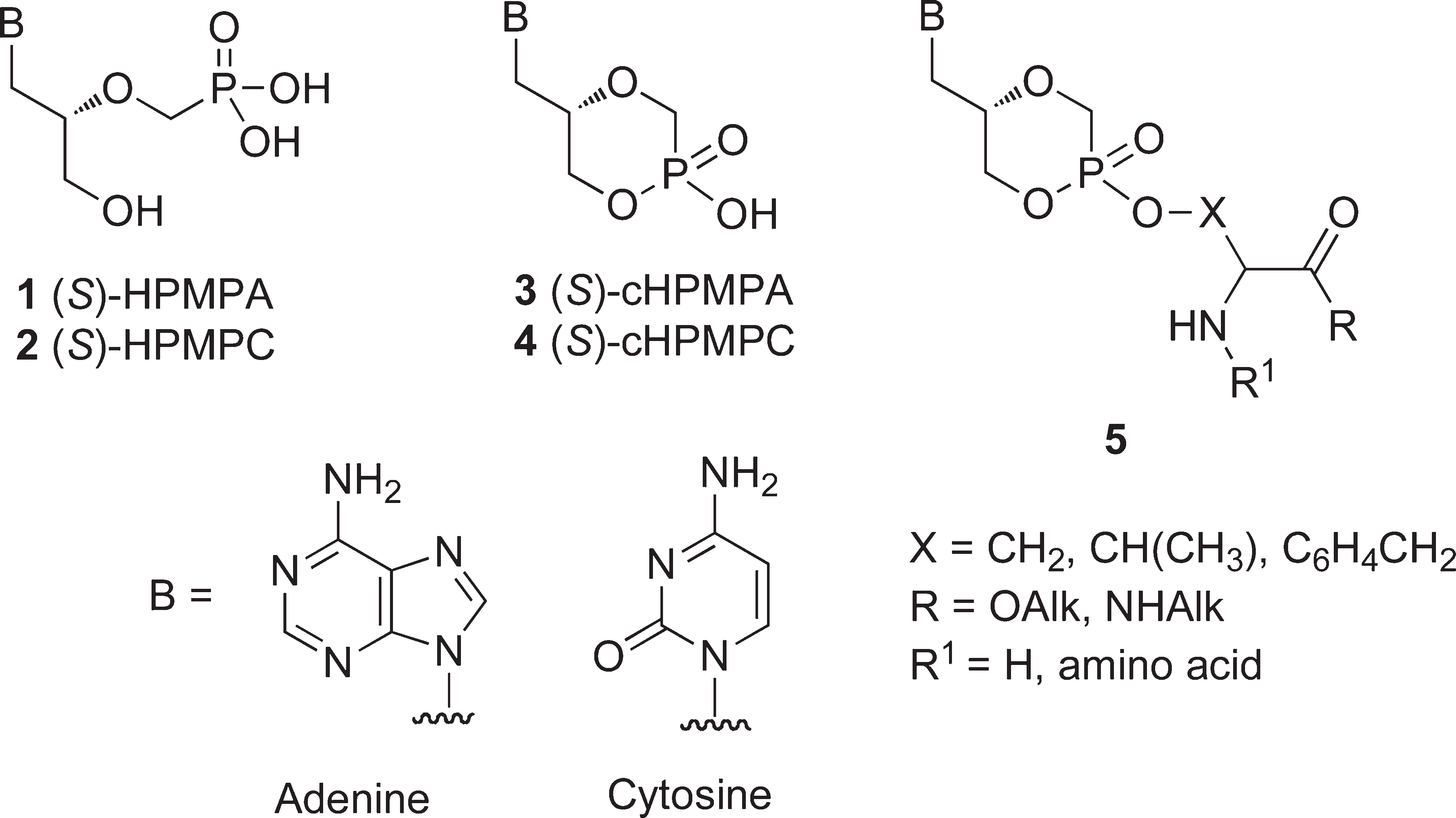
Structures of (S)-HPMPA (1), (S)-HPMPC (2), and their cyclic forms 3 and 4 and general structure of the amino acid/dipeptide ester prodrugs 5.
Related Questions and Answers
A: Cidofovir has demonstrated high efficacy in treating molluscum contagiosum, particularly in immunocompromised patients. For instance, a study reported complete resolution of lesions in patients treated with topical cidofovir 3% cream within 1 to 3 months. Intravenous cidofovir has also been successful in treating severe cases of molluscum contagiosum, with significant improvement observed in patients who had not responded to other treatments.
Q: What are the clinical outcomes of using cidofovir for treating verruca vulgaris and verruca plana?
A: Cidofovir has shown significant efficacy in treating verruca vulgaris and verruca plana, both topically and intralesionally. For example, a retrospective analysis of 58 patients with recalcitrant warts treated with intralesional cidofovir (15 mg/mL) reported that over 75% of patients achieved complete resolution after an average of 3.4 treatments administered monthly. Topical cidofovir has also been effective, with studies showing complete resolution in a significant number of patients, although some cases required longer treatment durations.
A: The side effects of cidofovir vary depending on the route of administration:
Topical: Common side effects include inflammation, erosion, or a burning sensation upon application. These are generally self-limited and localized.
Intralesional: Side effects include pain, burning, blistering, discoloration, swelling, and erosion. These reactions are also typically localized and self-limited.
Topical: Common side effects include inflammation, erosion, or a burning sensation upon application. These are generally self-limited and localized.
Intralesional: Side effects include pain, burning, blistering, discoloration, swelling, and erosion. These reactions are also typically localized and self-limited.
A: Cidofovir can be administered in several ways for cutaneous applications:
Topical: Commonly compounded as a 0.5% to 3% formulation in cream, ointment, or gel. It is applied daily or twice daily for at least 1 week up to 52 weeks.
Intralesional (IL): Diluted to concentrations ranging from 2.5 mg/mL to 37.5 mg/mL (most commonly 15 mg/mL) and injected directly into the lesion using serial puncture or crosshatching techniques.
Intravenous (IV): Used in cases of extensive disease or critical illness, with dosages ranging from 3.5 to 5 mg/kg, often administered with probenecid to reduce nephrotoxicity.
Topical: Commonly compounded as a 0.5% to 3% formulation in cream, ointment, or gel. It is applied daily or twice daily for at least 1 week up to 52 weeks.
Intralesional (IL): Diluted to concentrations ranging from 2.5 mg/mL to 37.5 mg/mL (most commonly 15 mg/mL) and injected directly into the lesion using serial puncture or crosshatching techniques.
Intravenous (IV): Used in cases of extensive disease or critical illness, with dosages ranging from 3.5 to 5 mg/kg, often administered with probenecid to reduce nephrotoxicity.
A: Cidofovir functions by specifically inhibiting viral DNA synthesis. It incorporates into the growing viral DNA strand, acting as a competitive inhibitor and alternative substrate for viral DNA polymerase, thereby blocking subsequent viral DNA synthesis. This mechanism is particularly effective against DNA viruses, including herpesviruses, papillomaviruses, and molluscum contagiosum virus.