Beta-Nitrostyrene
CAS number: 102-96-5
Beta-nitrostyrene appears as yellow prisms (from ethanol) or yellow crystalline solid.
Related images
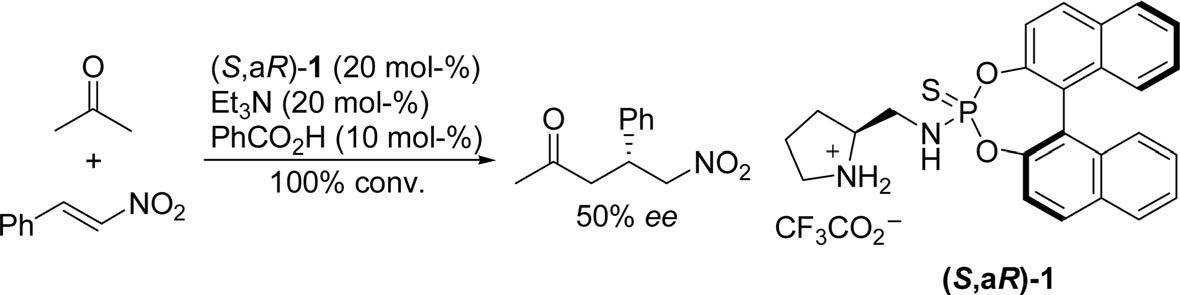
(S,aR)-1-catalyzed asymmetric Michael addition of acetone to β-nitrostyrene.
Related Questions and Answers
Q: Which β-nitrostyrene analogues were used to demonstrate the effectiveness of the NaBH₄/CuCl₂ system?
A: The β-nitrostyrene analogues used in the study include 2,5-dimethoxy-β-methyl-β-nitrostyrene (3a), 2,5-dimethoxy-β-nitrostyrene (4a), 2-(2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)ethan-1-amine (4b), 2-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-methylphenyl)ethan-1-amine (5b), and 2-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)ethan-1-amine (6b). These analogues were chosen to demonstrate the versatility and effectiveness of the NaBH₄/CuCl₂ system.
Q: What is the role of stainless steel electrodes in the electrochemical coupling of beta-nitrostyrene?
A: Stainless steel electrodes are chosen for their anti-corrosion properties and efficiency in the electrochemical reduction process. They provide a suitable surface for electron transfer, leading to the reduction and dimerization of beta-nitrostyrene with high yield and selectivity.
A: Beta-nitrostyrene undergoes electrochemical reduction and dimerization under constant-current conditions, leading to the formation of 1,4-dinitro-2,3-diphenylbutane and related derivatives. A study explores its electrochemical behavior, optimization of reaction conditions, and the mechanism of its reduction and coupling.