Coumarin
CAS number: 91-64-5
Coumarin is a chromenone having the keto group located at the 2-position. It has a role as a fluorescent dye, a plant metabolite and a human metabolite. Coumarin and its derivatives possess anticancer activity against different types of cancers such as prostate, renal, breast, laryngeal, lung, colon, CNS, leukemia, malignant melanoma.
Related images
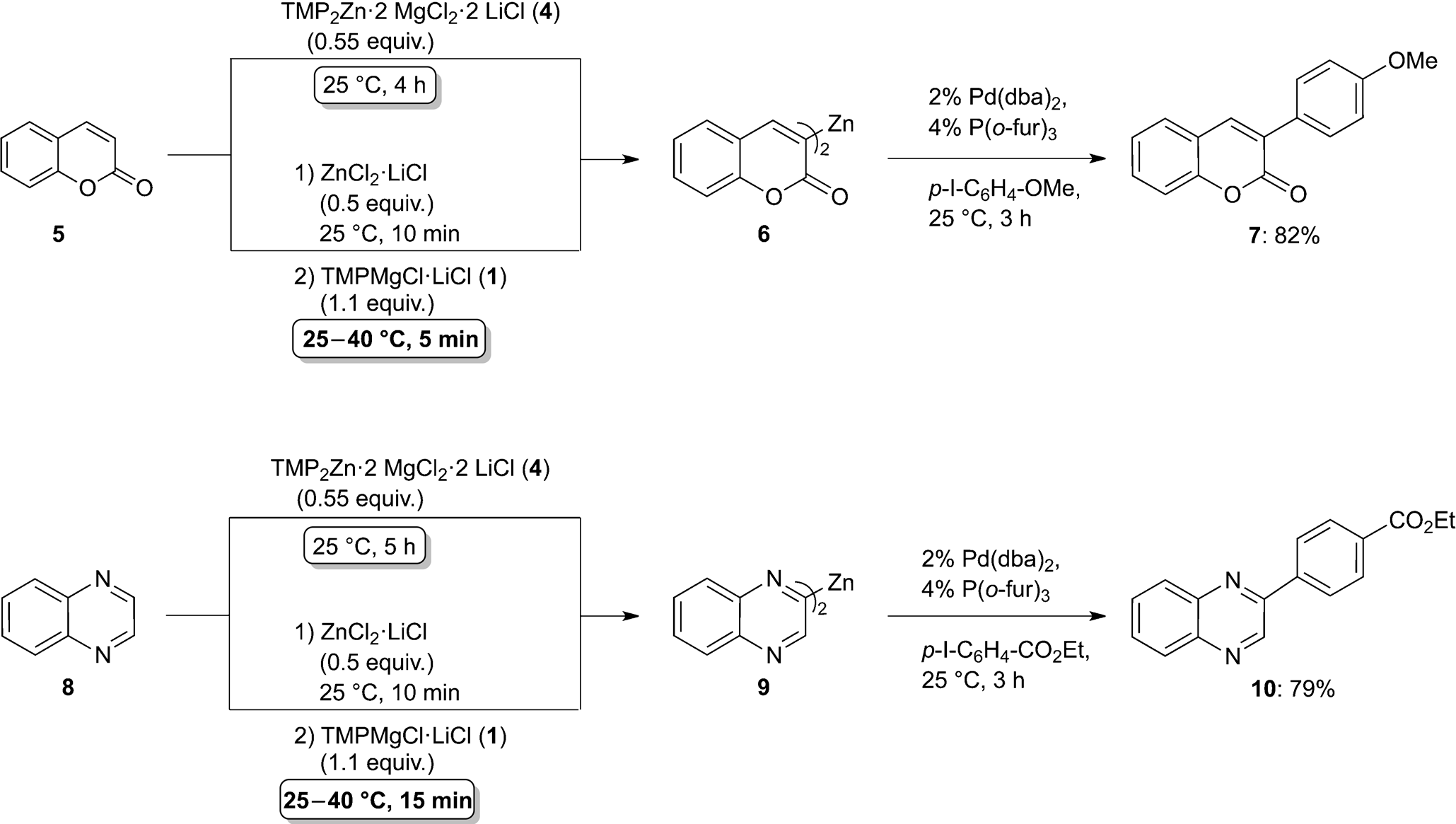
Dramatic acceleration of the metalation of coumarin (5) and quinoxaline (8) with TMP2Zn·2MgCl2·2LiCl (4) and the new sequential procedure.
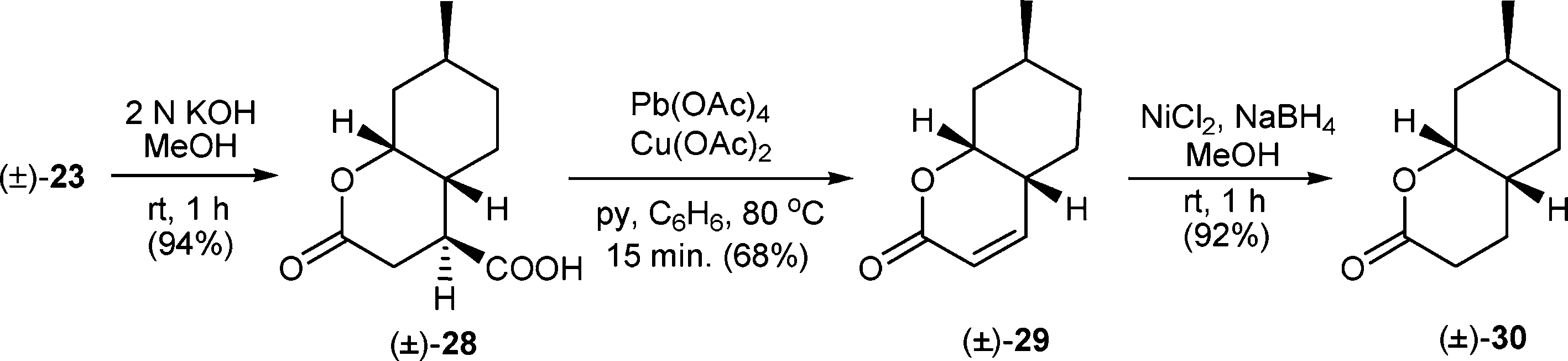
Ring expansion of γ-lactone to δ-lactone: Synthesis of chromenone
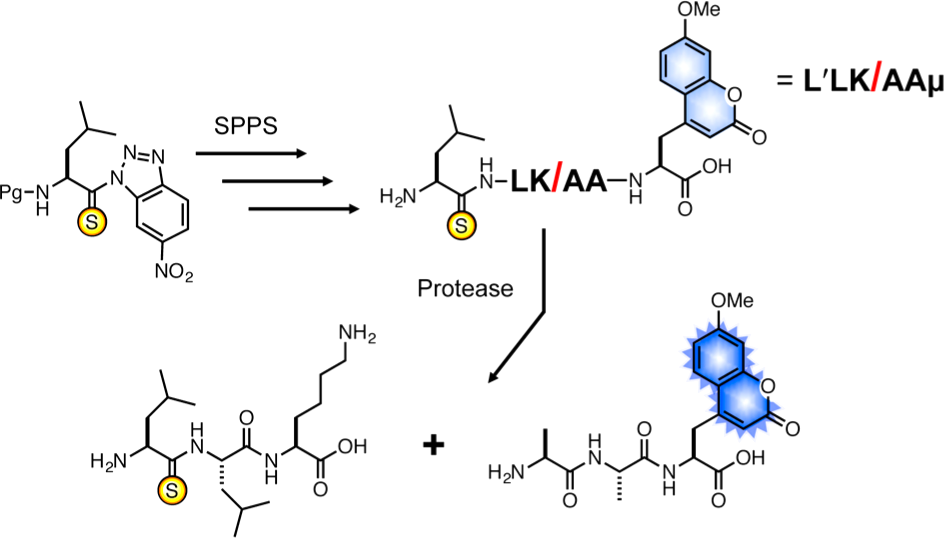
Profluorescent thiopeptides for monitoring protease activity. Thioamide (denoted by the one or three letter code of the corresponding natural amino acid with a prime symbol, e.g., L′) substrates can be prepared on solid phase from benzotriazole precursors and fluorescent amino acids such as 7-methoxycoumarin-4-ylalanine (μ). Incubation of a coumarin/thioamide labeled peptide with a protease results in cleavage and a concomitant gain of fluorescence.
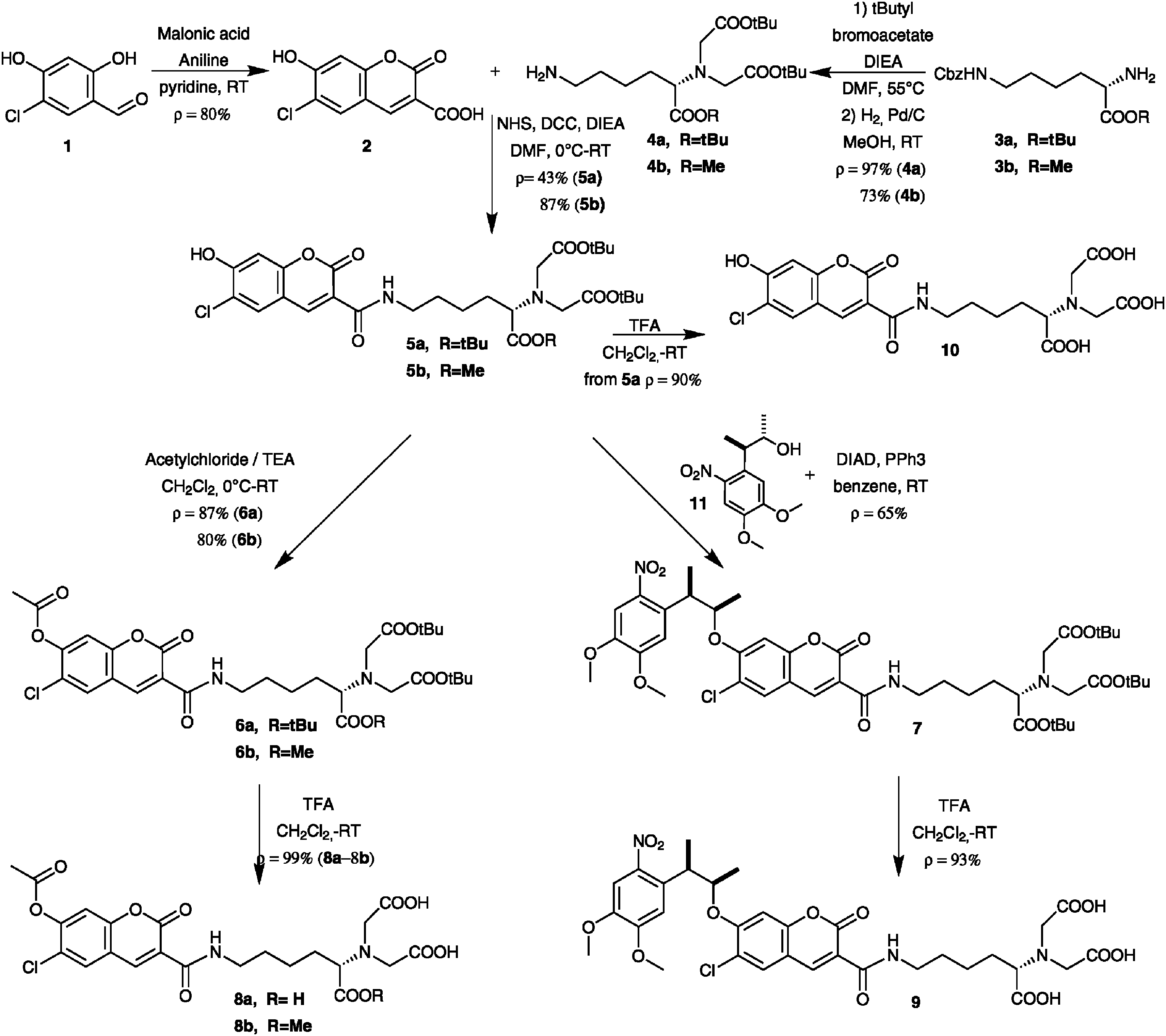
Synthesis of 7-DMNPB-coumarin-NTA, 7-acetylcoumarin-NTA and 7-acetylcoumarin-NDA.

Palladium-catalyzed C–H bond activation–carbonylation of 2-arylphenols for syntheses of benzopyranones.
Related Questions and Answers
No related questions yet