Coenzyme A
CAS number: 85-61-0
Coenzyme A (CoA) is an essential cofactor in all living organisms. It is defined as a crucial cofactor in metabolism that is synthesized through a bifunctional enzyme encoded by the COASY gene, which catalyzes the final steps of its biosynthesis, essential for human cellular function.
Related images
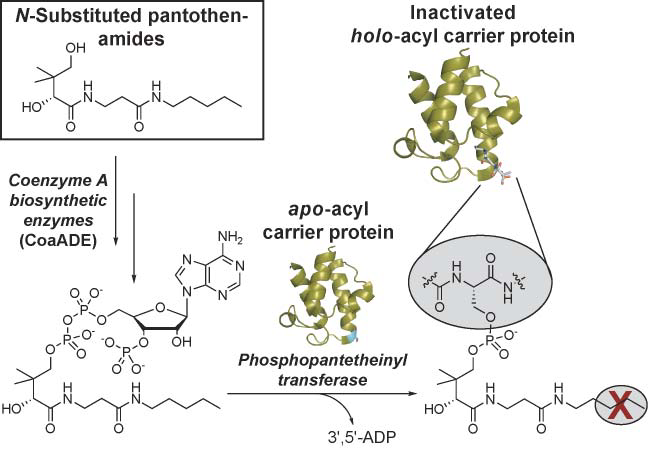
N-Substituted pantothenamides (such as N-pentyl pan- tothenamide shown above) act as antimetabolites by forming coenzyme A analogues which do not contain the essential terminal thiol group of natural CoA. These analogues subsequently transfer inactive prosthetic groups to the acyl carrier proteins that are involved in fatty acid metabolism, thereby blocking these processes.
Related Questions and Answers
No related questions yet