Water-d₂
CAS number: 7789-20-0
Water-d₂, also known as heavy water, contains two deuterium atoms bonded to one oxygen atom. This substitution makes heavy water about 10% denser than normal water and alters some of its physical and chemical properties, such as a higher boiling point (101.4 °C) and melting point (3.8 °C). D₂O is primarily used as a neutron moderator in nuclear reactors, where it slows down neutrons without capturing them, enhancing the efficiency of nuclear fission. It is also utilized in certain analytical and spectroscopic techniques, including NMR, due to its unique nuclear properties.
Related images
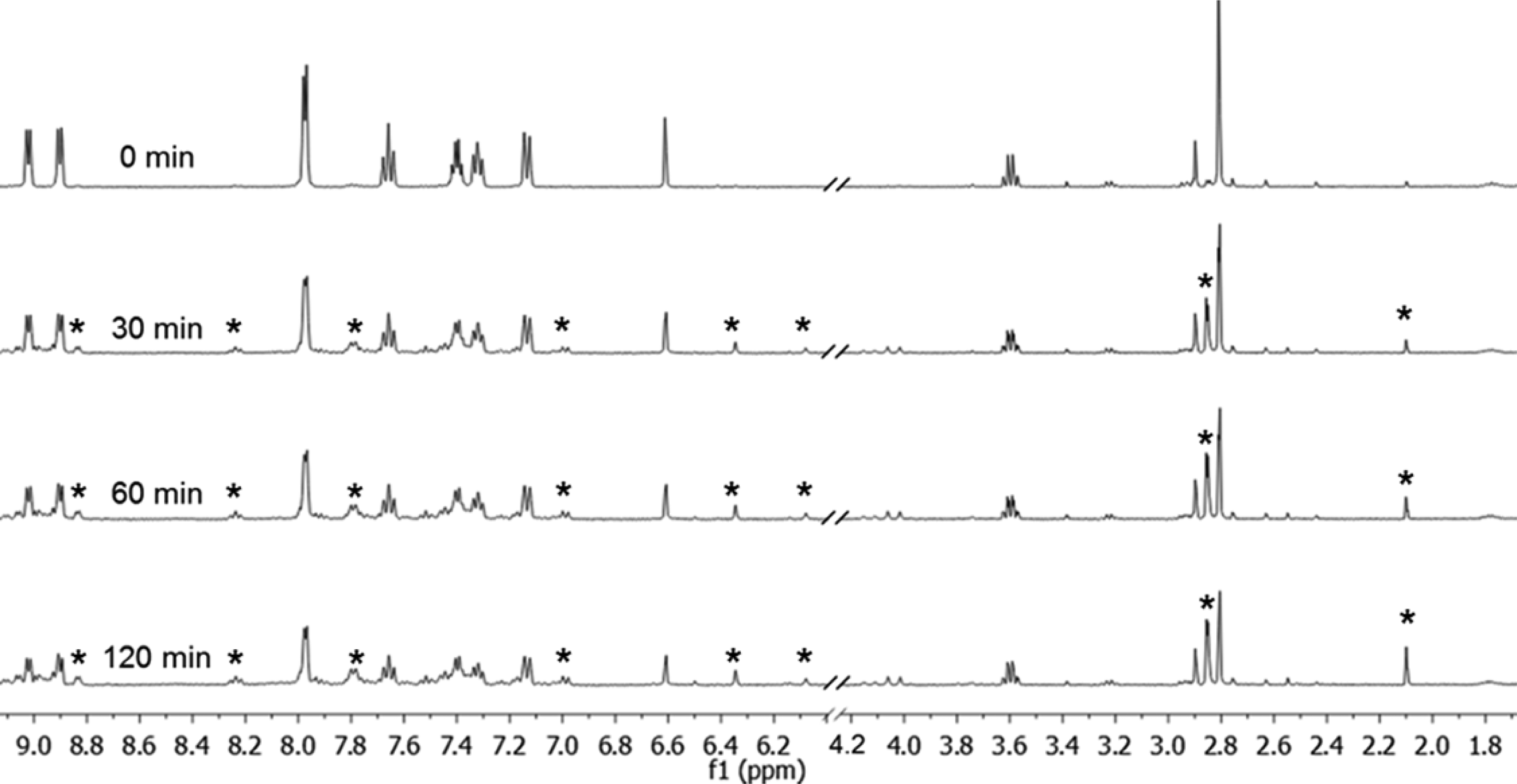
1H NMR spectra following irradiation of 13 in D2O with λirr ≥ 395 nm for 0, 30, 60, and 120 min. Stars indicate new signals evolved upon irradiation.
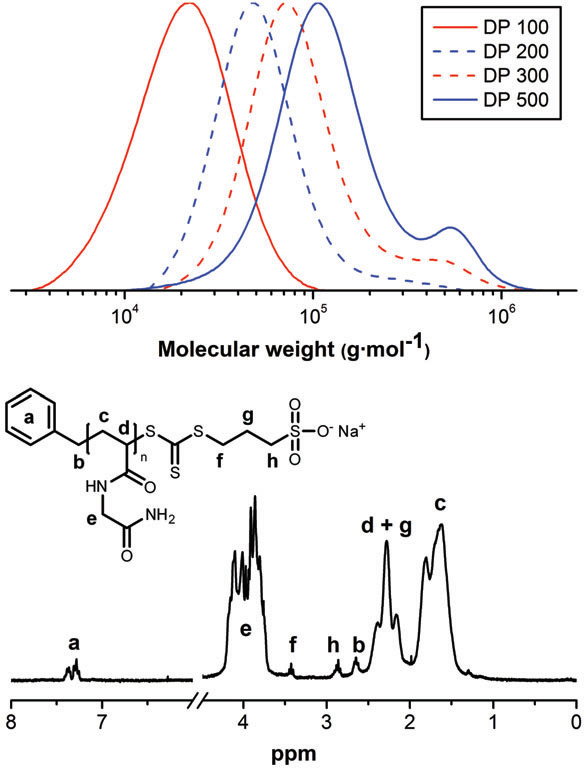
Molecular characterization of homopolymers of 1 prepared by RAFT polymerization: (top) SEC chromatograms of different DPn samples recorded at 70 1C in DMSO; (bottom) H NMR spectrum of the homopolymer of 1 with an average chain length of 100 Å recorded in D2O.
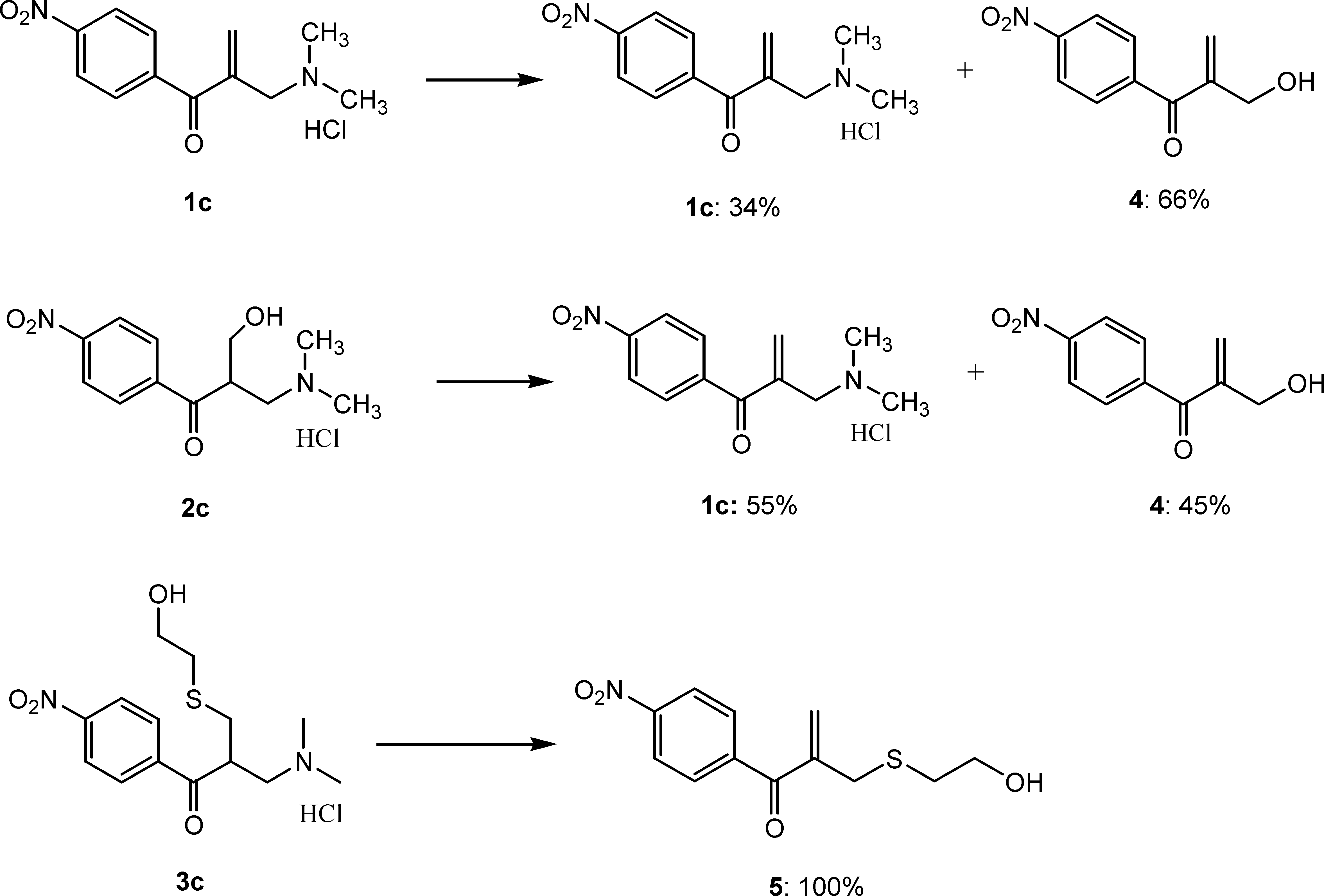
Stability of 1c, 2c and 3c after Incubation in Deuterium Oxide at 37 °C for 48 h.
Related Questions and Answers
No related questions yet