Salicylic acid
CAS number: 69-72-7
Salicylic acid is a beta hydroxy acid (BHA) primarily known for its use in skincare, particularly for treating acne and other skin conditions.
Related images
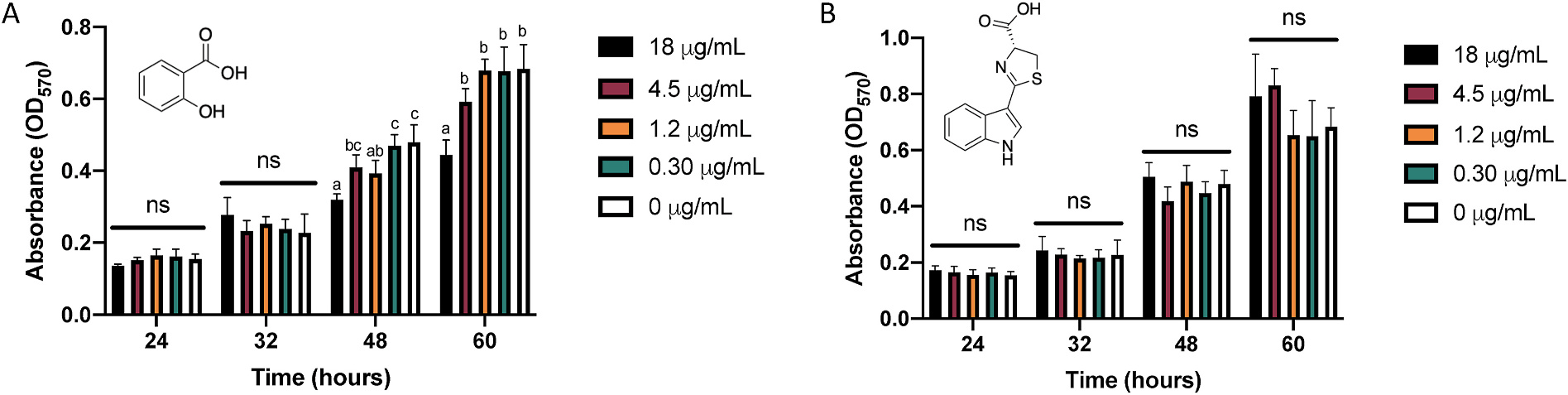
Effects of dihydrocarbamazepine (DHCA) and salicylic acid (SA) on biofilm formation of Pseudomonas syringae (Pst) in vitro
Related Questions and Answers
A: The study found that the most notable effect of the irrigation treatments was the reduction in the concentration of different amino acids caused by the 50/100 treatment in white chard. In contrast, the 50F/50D treatment in red chard resulted in increases in certain amino acids like Phe, Glu, and Arg. The application of SA had varying effects, with the most significant changes observed in white chard irrigated with the 50F/50D treatment, which led to an increase in Glu and a decrease in Ile and Ala. These results suggest that SA and irrigation treatments can influence the amino acid profile of Swiss chard, potentially affecting its nutritional quality.
A: The study found that the 50/100 treatment tended to reduce lipid peroxidation in both white and red chard, although the reduction was not statistically significant in red chard. The application of SA resulted in significant changes only in red chard irrigated with the 50F/50D and 50/100 treatments, where SA increased lipid peroxidation. These results suggest that the SA concentration used may not have been optimal for red chard, as it led to increased oxidative stress. In contrast, the 50/100 treatment without SA showed a tendency to reduce lipid peroxidation, indicating better antioxidant defense mechanisms in the plant.
A: The study found that the total phenolic content showed little variability and was not significantly influenced by the irrigation treatments. However, the application of SA had varying effects depending on the irrigation treatment. For instance, SA combined with the 50/100 treatment increased total phenolic content in white chard. Regarding antioxidant activity, no significant effects were observed from the applied treatments. Red chard exhibited higher antioxidant activity compared to white chard, likely due to its higher concentration of betalains. These findings suggest that SA can influence phenolic content and antioxidant activity, but the effects depend on the specific irrigation treatment and chard variety.
A: The study found that the 50/100 treatment caused a reduction in chlorophyll a and β-carotene levels in both white and red chard varieties. However, the 50F/50D treatment increased chlorophyll b levels in both chard varieties. The application of SA had varying effects: it decreased chlorophyll a and β-carotene levels in plants irrigated with 100S, but increased chlorophyll b in red chard. These results suggest that SA can influence photosynthetic pigment levels, potentially affecting photosynthetic efficiency and plant growth, depending on the irrigation treatment and chard variety.
A: The study found that the application of salicylic acid (SA) had varying effects on the growth and quality of Swiss chard, depending on the irrigation strategy and the color of the chard. The white chard variety responded more favorably to the treatments, particularly with the 50/100+SA treatment, which resulted in greater plant weight, higher total phenolic content, and lower lipid peroxidation. In contrast, the red chard variety showed poor tolerance to the applied dose of SA. The findings suggest that SA can enhance the growth and nutritional quality of white chard under specific irrigation conditions in an aquaponic system.