1,2,3-Trioxolane
CAS number: 6669-36-9
1,2,3-Trioxolane is a cyclic organic peroxide with a three-membered ring containing three oxygen atoms. It is also known as a molozonide and is an unstable intermediate formed during the ozonolysis of alkenes. This unstable intermediate quickly rearranges to form the more stable 1,2,4-trioxolane (ozonide).
Related images
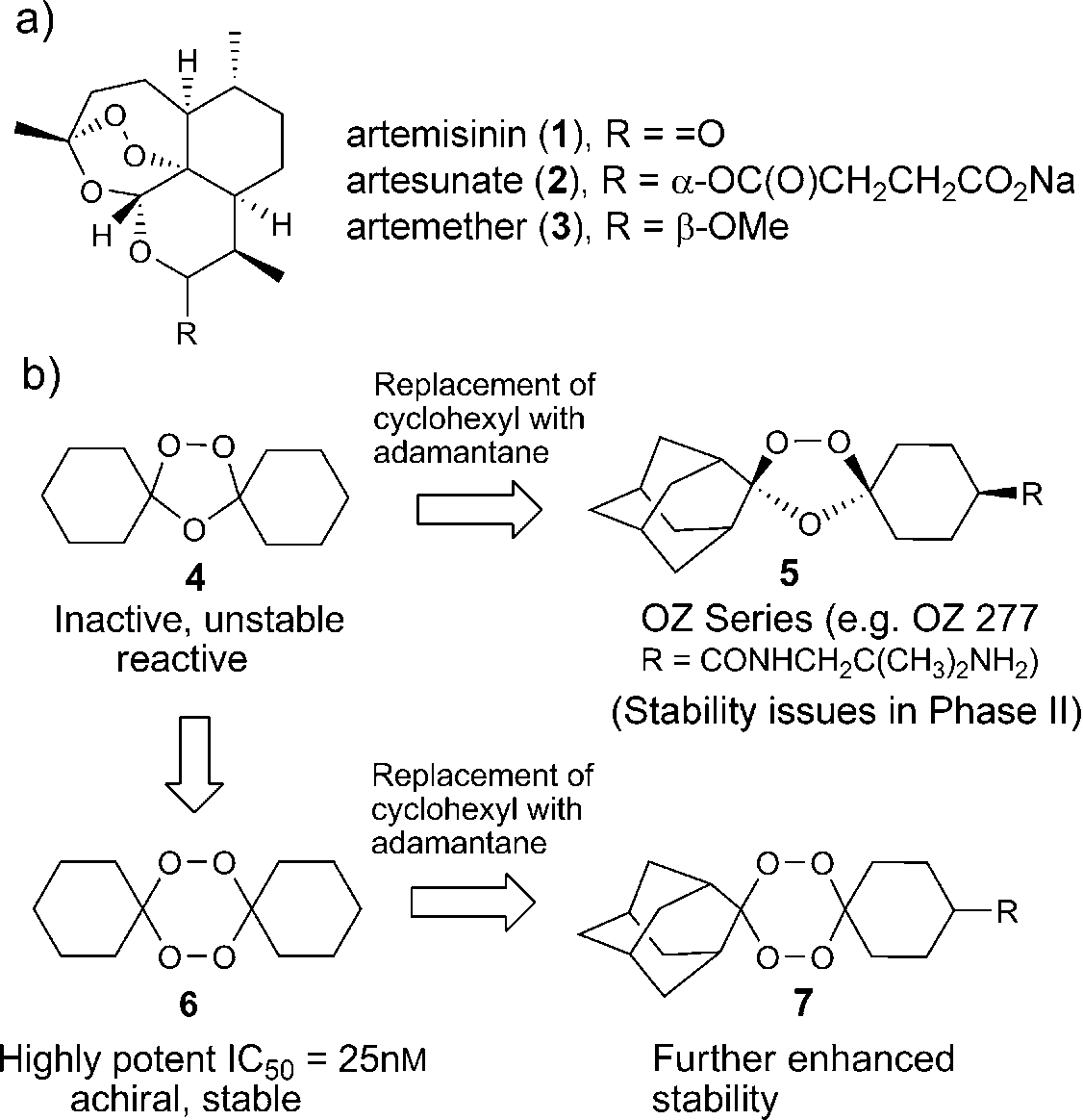
a) Artemisinin and its semisynthetic analogues. b) Comparison of tetraoxanes with trioxolane-based antimalarials.
Related Questions and Answers
No related questions yet