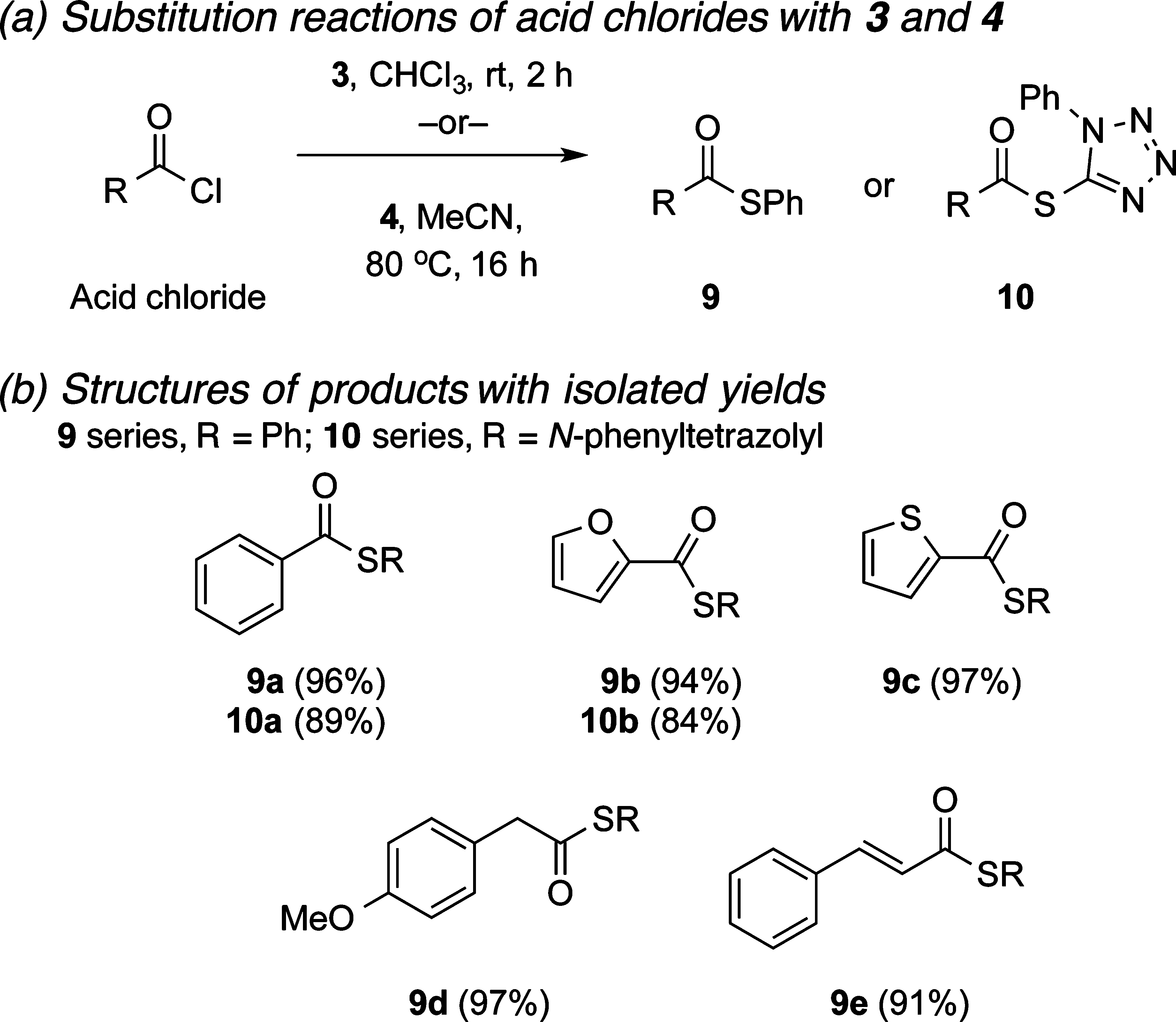
Acid chloride
CAS number: 63990-57-8
Acid chloride, also known as Acetyl chloride, (2,4-bis(1-methylbutyl)phenoxy)-, is an organic compound characterized by the presence of an acyl chloride functional group attached to a substituted phenoxy ring. The phenoxy moiety is substituted at the 2 and 4 positions with two 1-methylbutyl (isopentyl) groups, which are branched alkyl chains.
Related images
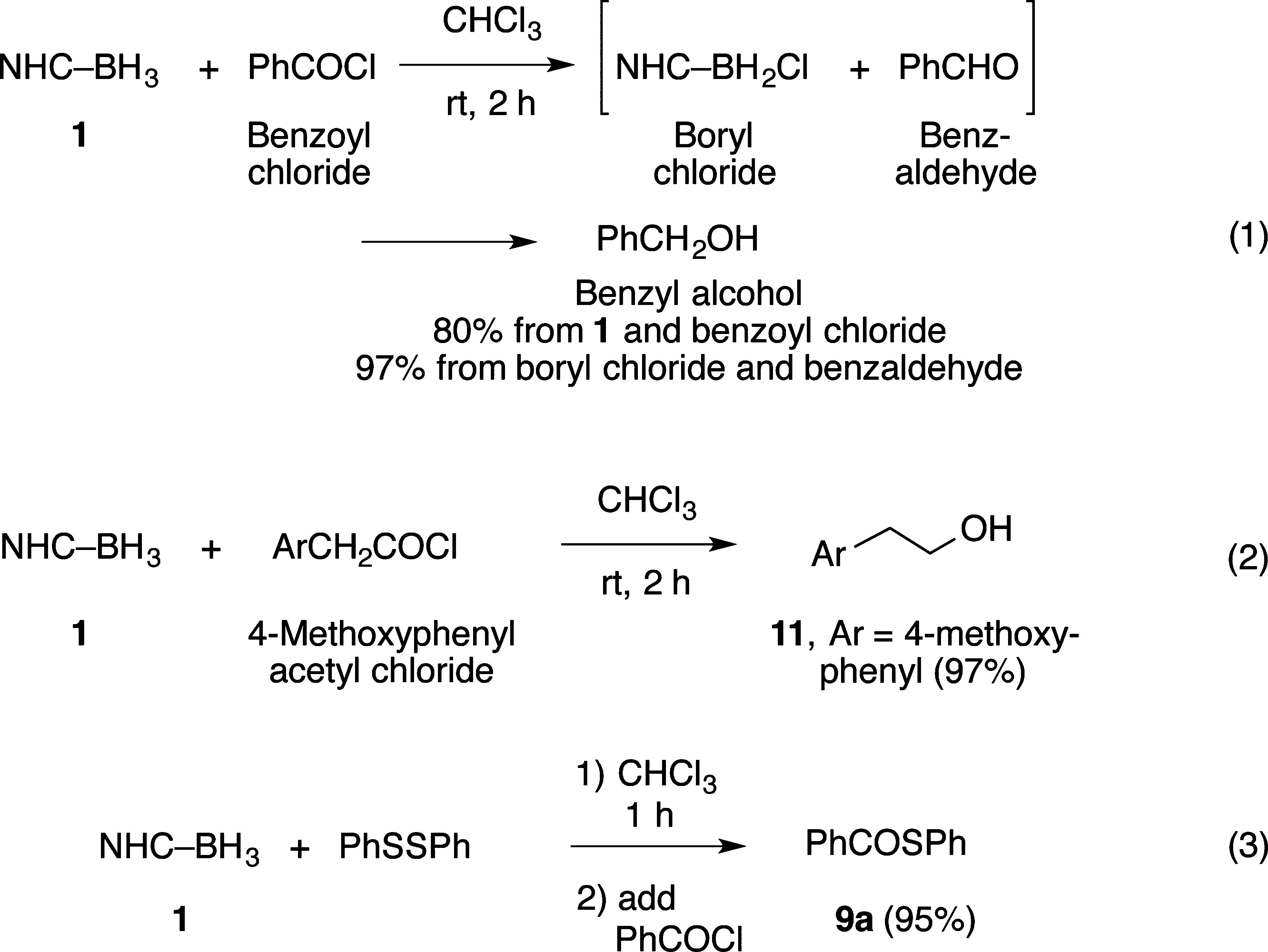
Results with acid chlorides depend on the order of addition: mixing everything, eqs 1 and 2, gives reduction; stepwise addition, eq 3, gives substitution.
Related Questions and Answers
No related questions yet