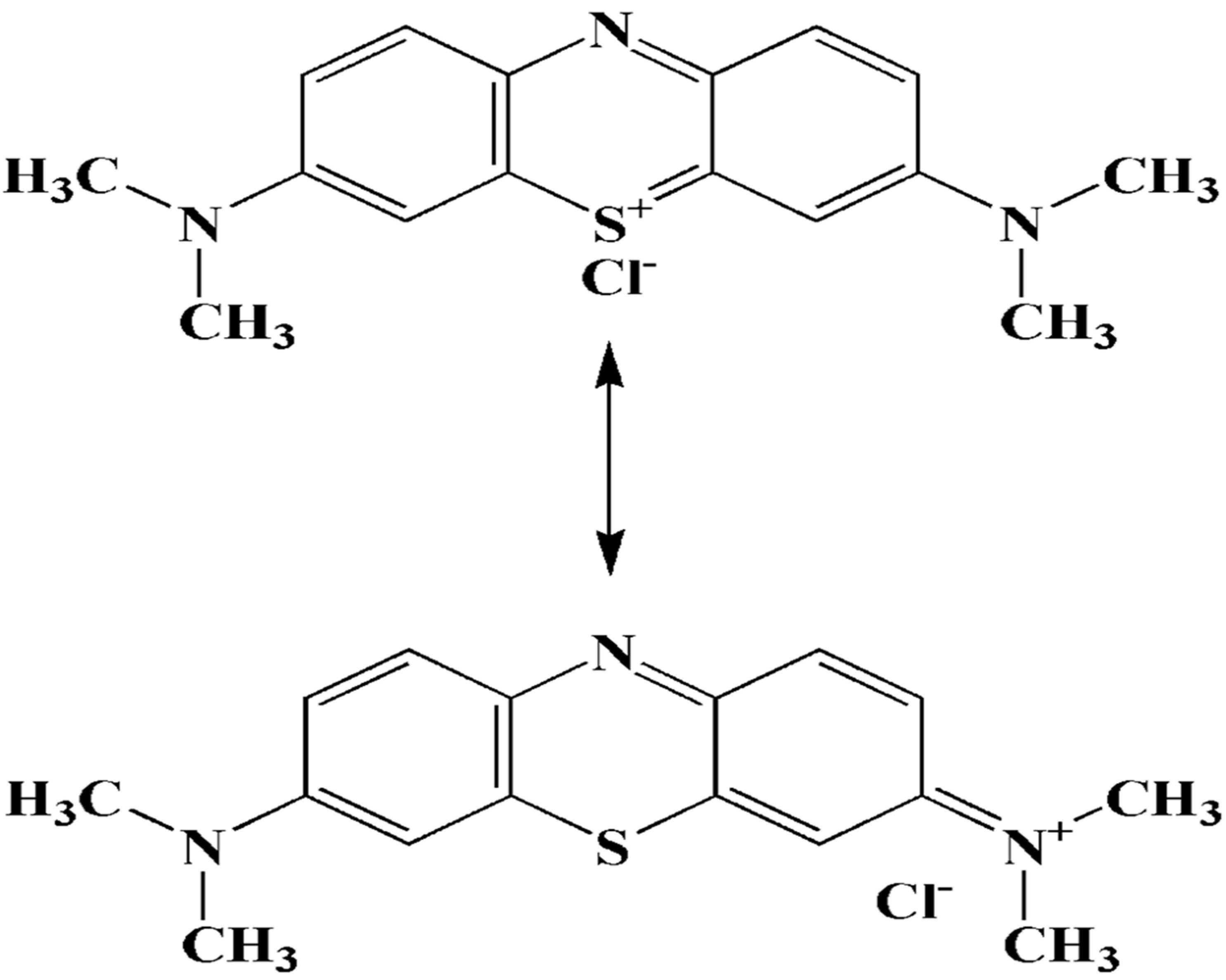
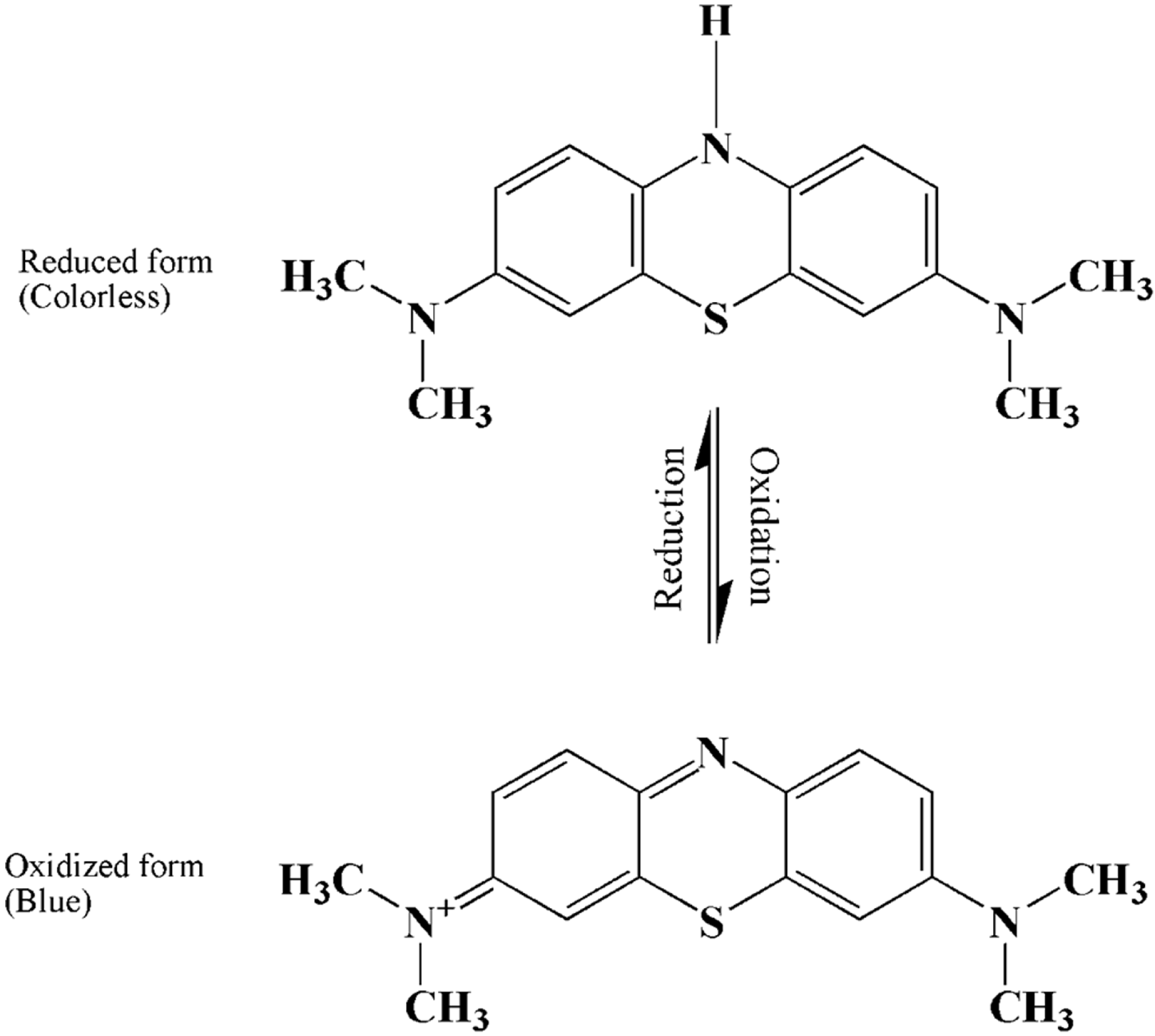
Methylene blue
CAS number: 61-73-4
Methylene blue is an organic chloride salt having 3,7-bis(dimethylamino)phenothiazin-5-ium as the counterion.
Related images
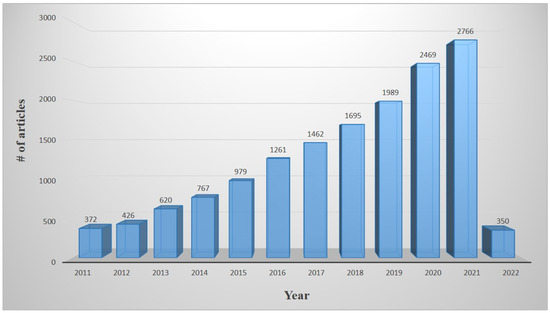
The Scopus database indicates that Methylene blue (MB) is widely utilized for various applications. The number of articles on MB dye degradation has been continuously increasing since 2010–2020, as shown in Figure 1.

The model and the structure of methylene blue (MB) dye molecule (Adapted with permission from the Royal. Society of Chemistry (license ID 1079849-1).

Proposed photocatalytic mechanism of ZnO-NPs for the catalytic degradation of MB dye
Related Questions and Answers
A: Methylene blue (MB) dye causes water quality problems due to its aromatic structure, resistance to biodegradation, environmental persistence, and toxicity to aquatic animals and human health. Its toxicity in humans can lead to effects such as cyanosis, vomiting, shock, increased heart rate, and diarrhea.
A: Intervention strategies are critical for managing methylene blue-containing wastewater to reduce potential harm to environmental and human health. Adsorption has emerged as a practical and effective method for removing methylene blue from wastewater by binding MB molecules to solid surfaces called adsorbents. Various materials, including activated carbons, metal-organic frameworks, charcoal, and agriculture waste-derived compounds, have been explored as methylene blue adsorbents. This study specifically focuses on the use of both treated and untreated adsorbents derived from discarded fruit seeds. Biowaste fruit seeds offer a low-cost alternative to commercial activated carbon for effective, large-scale removal of various pollutants from aquatic environments.
A: A geopolymer composite, synthesized from laterite and recycled beer bottle glass, was developed and optimized for the adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solutions. The optimal synthesis conditions achieved a high methylene blue index of 74.87 mg/g. Batch adsorption experiments demonstrated a maximum methylene blue adsorption capacity of 12.63 mg/g, aligning with the Langmuir isotherm and pseudo-second-order kinetic model, which suggests monolayer chemisorption. This indicates the geopolymer's potential as an efficient and sustainable adsorbent for dye removal.