α-Kainic acid
CAS number: 487-79-6
Kainic acid is a dicarboxylic acid, a pyrrolidinecarboxylic acid, a L-proline derivative and a non-proteinogenic L-alpha-amino acid. α-Kainic acid is a neuroexcitatory molecule and a cyclic analog of L-glutamate, first isolated from the marine alga Digenea simplex. It's a key member of the kainoid family and is used in neuropharmacology research to mimic neurological disorders like epilepsy, Alzheimer's, and Huntington's disease.
Related images
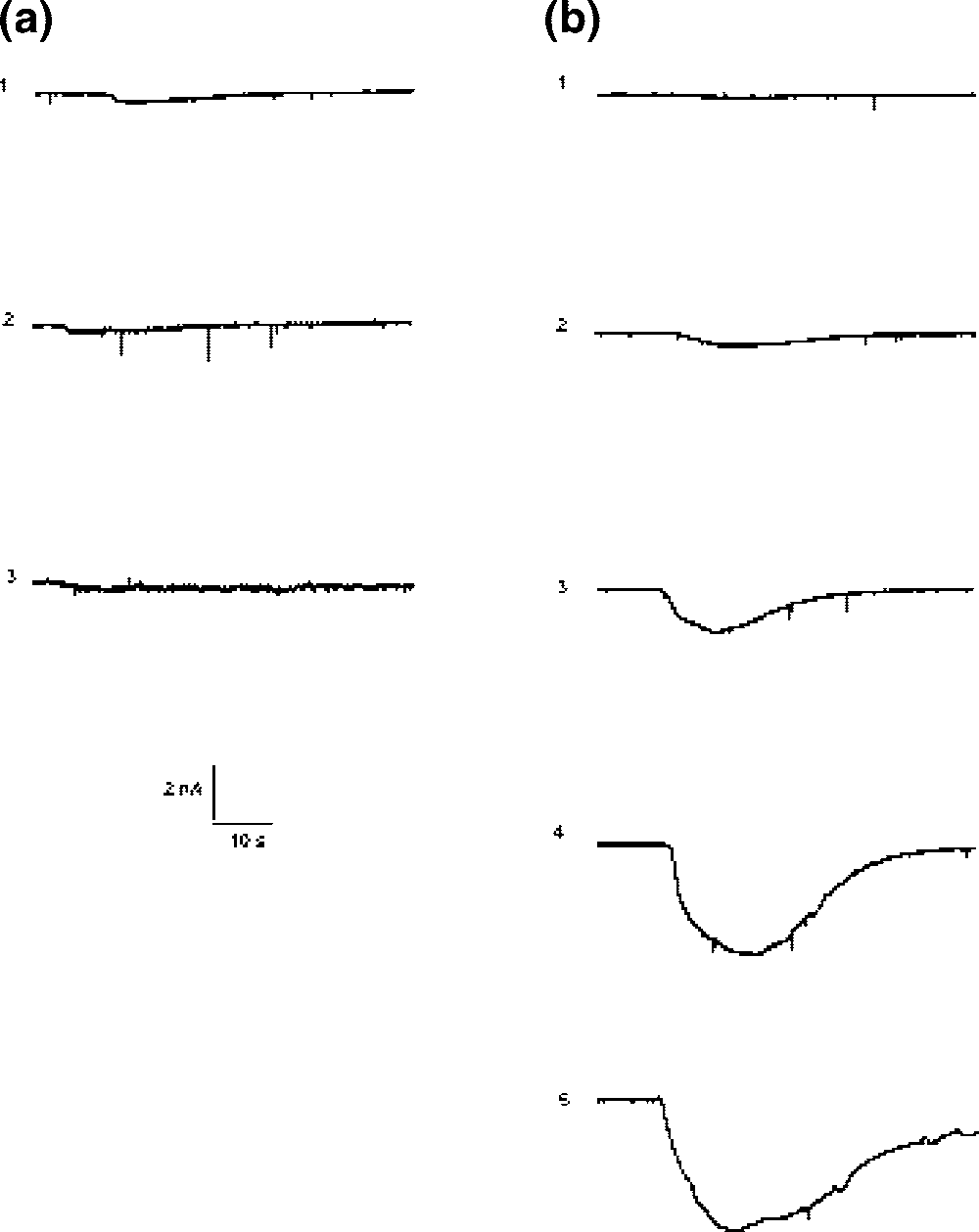
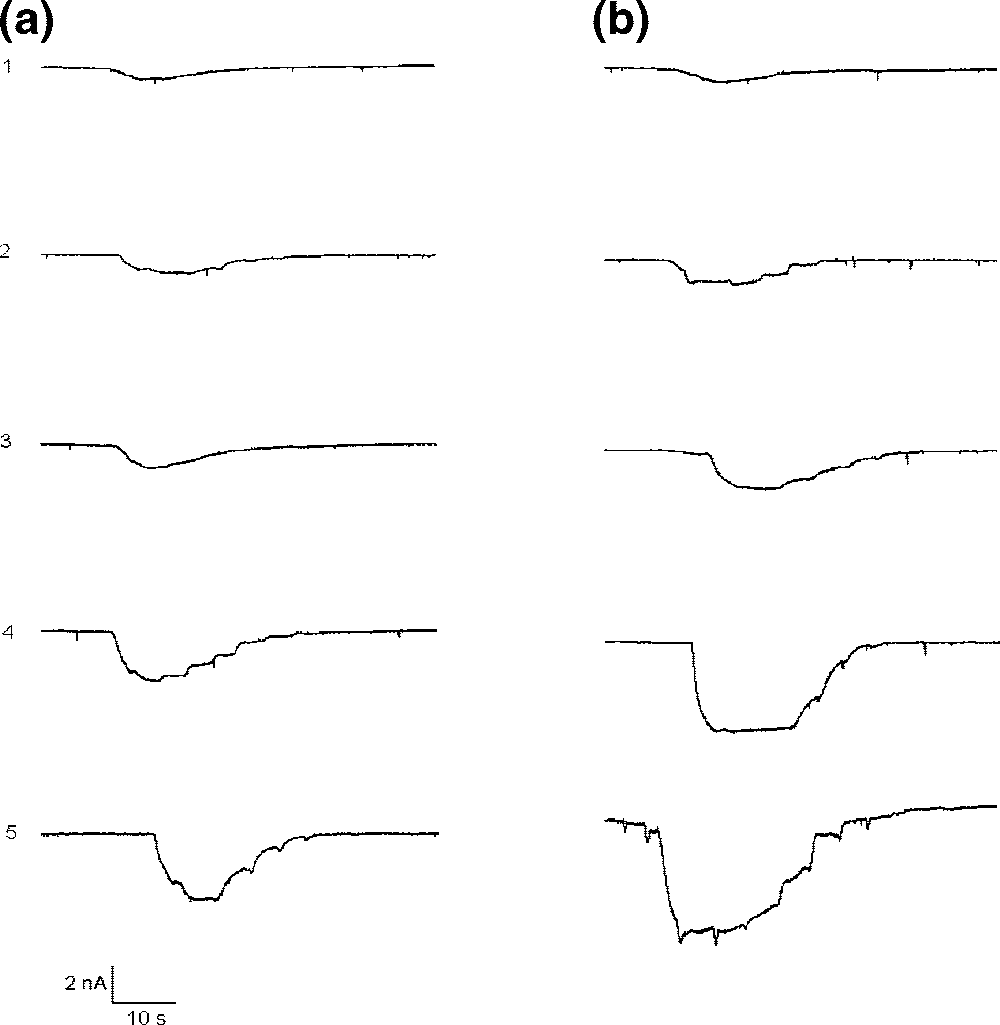
Transmembrane currents induced in Purkinje neurons by different doses of glutamate and kainic acid (KA).
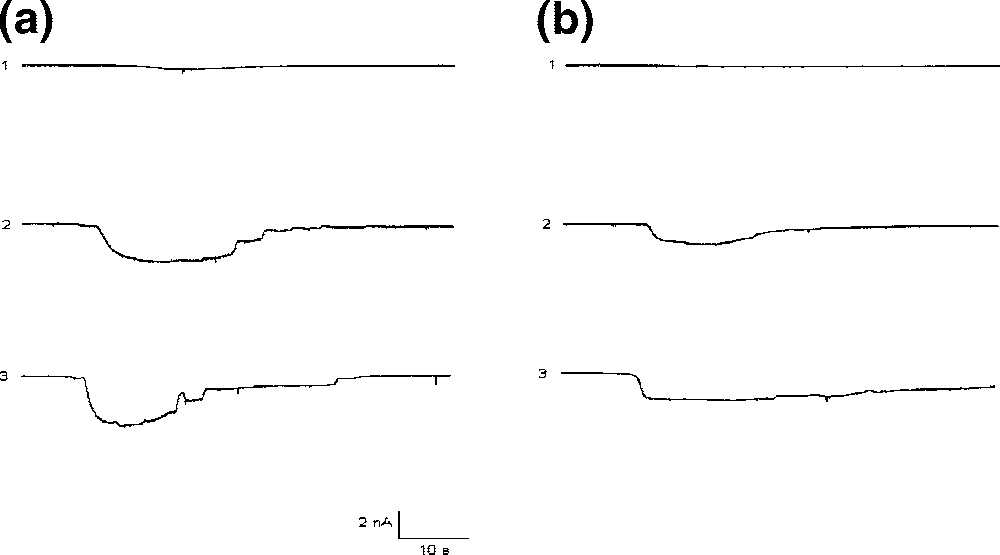
Comparative potentiation of kainic acid (KA) and glutamate responses in Purkinje neurons by CT and 3.
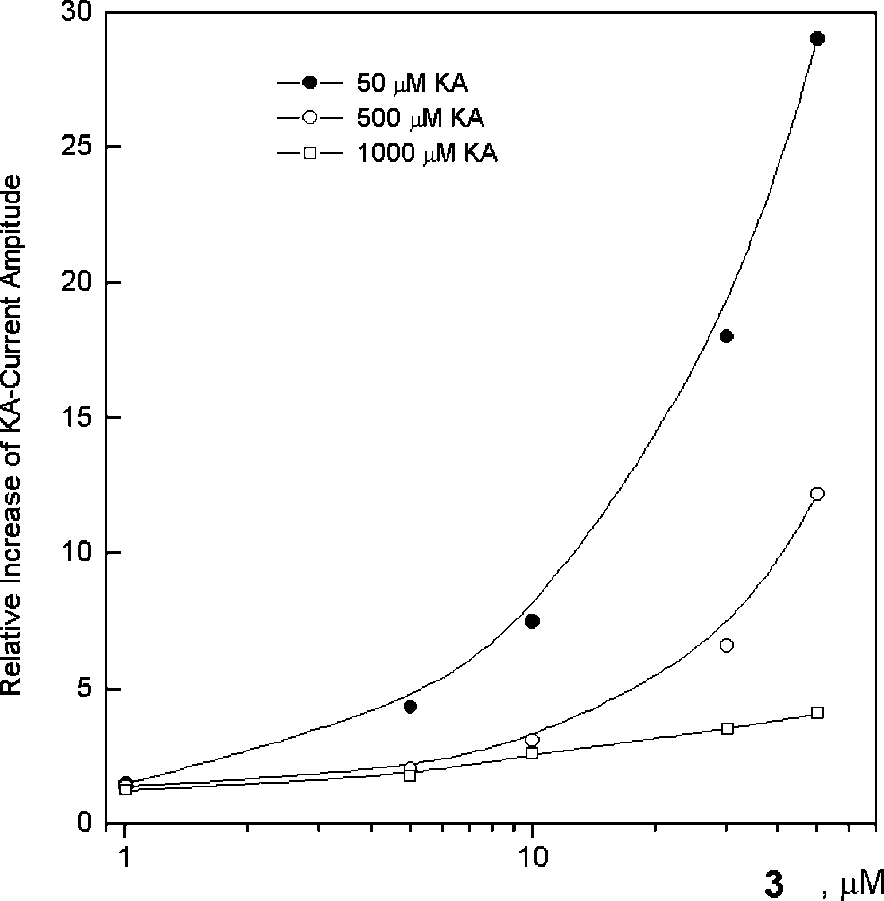
Concentration dependence of 3 effect on the currents induced by different kainate doses.
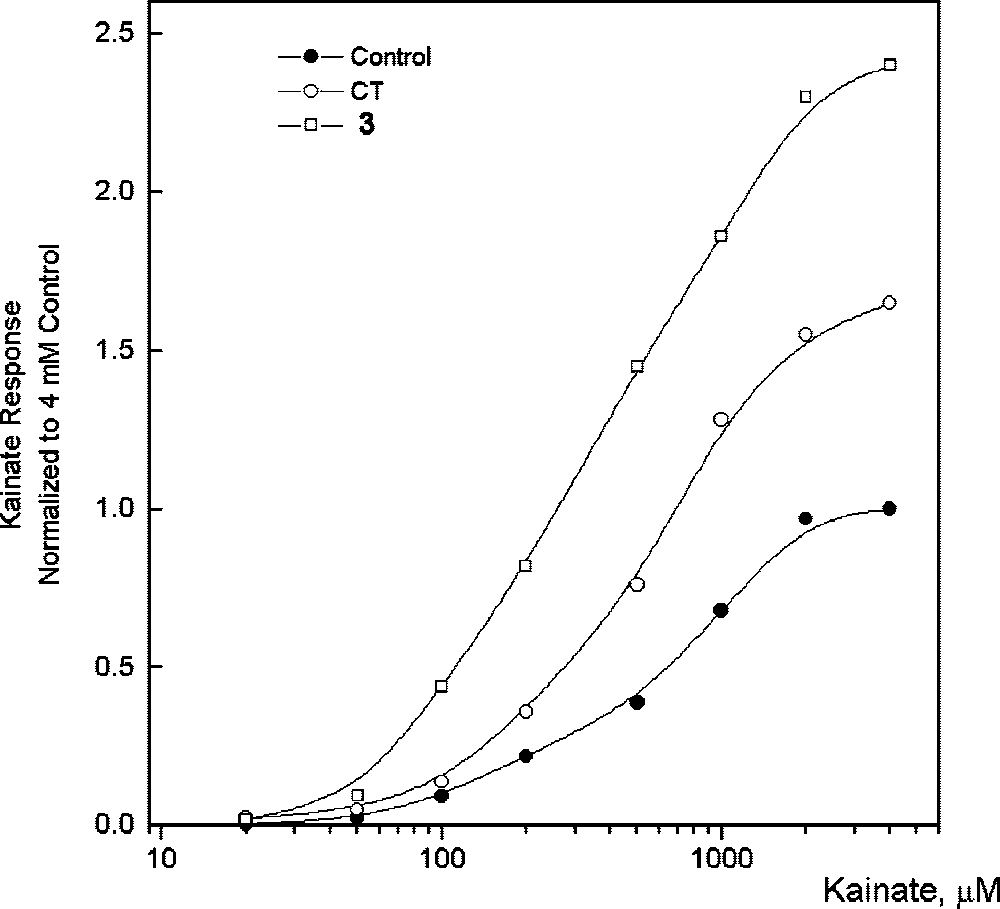
Effect of CT (cyclothiazide) and 3 on dose-dependent response for the currents induced by kainic acid in Purkinje neurons.
Comparative effect of different doses of CT (cyclothiazide) and 1 on currents, induced by the fixed concentration of kainic acid (KA).
Related Questions and Answers
No related questions yet