Triphosgene
CAS number: 32315-10-9
Triphosgene, also known as bis(trichloromethyl) carbonate, is a chemical compound used as a reagent in organic synthesis, particularly as a safer alternative to the toxic gas phosgene. It's a white, crystalline solid that decomposes to release phosgene at elevated temperatures. This makes it a convenient and safer way to introduce carbonyl groups into molecules.
Related images
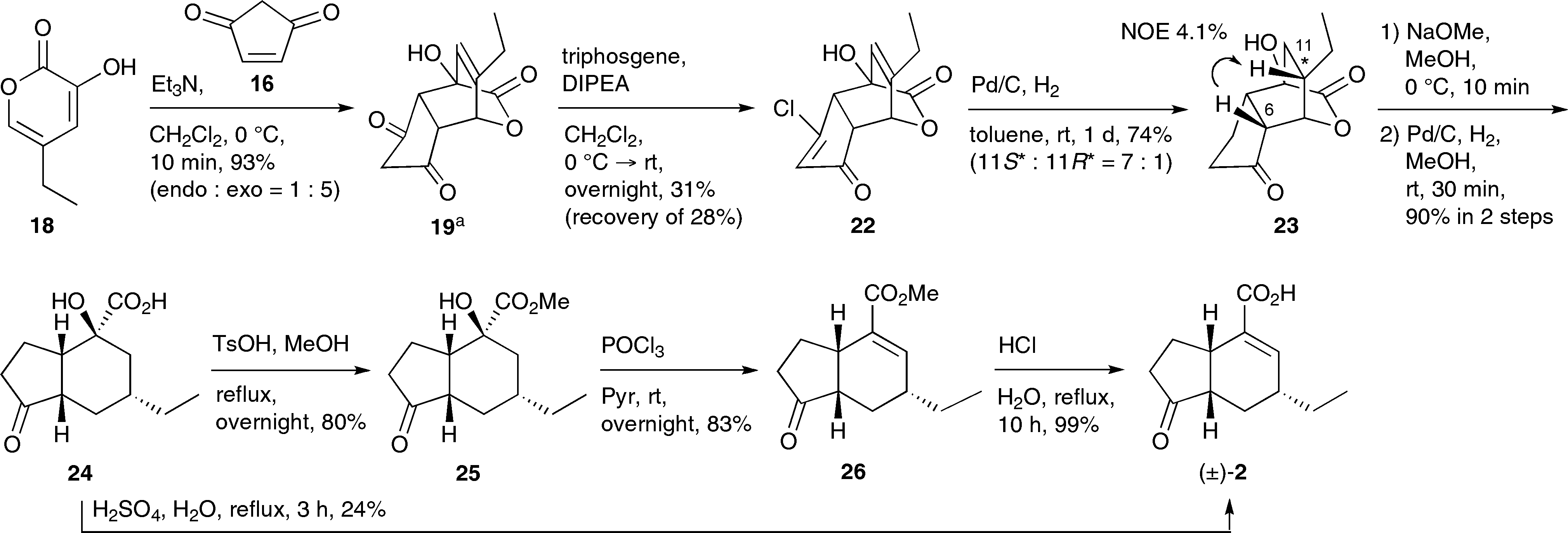
Synthesis of coronafacic acid ( )-2. The product was obtained as a Et3N salt.
Related Questions and Answers
No related questions yet