4-(2-hydroxyethoxy)benzaldehyde
CAS number: 22042-73-5
4-(2-Hydroxyethoxy)benzaldehyde, also known as Benzaldehyde, 4-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-, is an aromatic aldehyde featuring a benzene ring substituted at the para position with a 2-hydroxyethoxy group (–OCH₂CH₂OH) and bearing an aldehyde group (–CHO) directly attached to the ring. Its molecular formula is C₉H₁₀O₃, and it appears as a pale yellow to colorless crystalline solid or liquid with a mild, sweet, and slightly floral odor, reminiscent of other benzaldehyde derivatives. The presence of both hydroxyl and aldehyde functionalities gives it interesting reactivity, enabling it to participate in condensation, acetal formation, and esterification reactions, while the ether linkage contributes to its solubility in polar organic solvents.
Related images
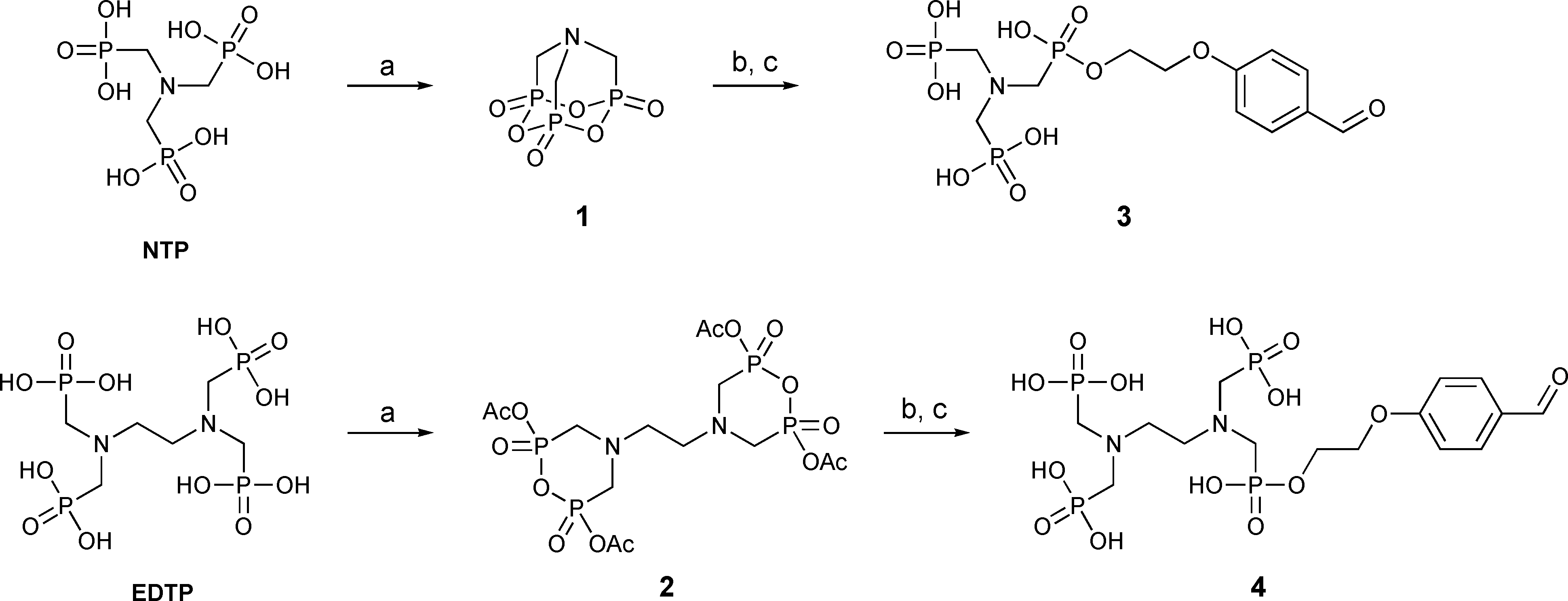
Preparation of the multiphosphonate building blocks 3 and 4. Reagents and conditions: a) acetic anhydride, DMF, b) 4-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-benzaldehyde, DMSO, c) water, DMSO.
Related Questions and Answers
No related questions yet