(2E)-3-Phenyl-2-propenenitrile
CAS number: 1885-38-7
(2E)-3-Phenyl-2-propenenitrile, also known as cinnamonitrile or (E)-cinnamyl nitrile. Structurally, it consists of a phenyl group (C₆H₅–) attached to a propenenitrile chain (CH=CH–CN), where the double bond between the second and third carbon atoms is in the E (trans) configuration. This gives the molecule a linear geometry across the double bond, contributing to its stability and unique chemical reactivity. It appears as a colorless to pale yellow liquid and is used primarily as an intermediate in organic synthesis, including the production of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and fragrances. Its nitrile group contributes to moderate polarity and can participate in various chemical transformations such as reduction, hydrolysis, or cyclization.
Related images
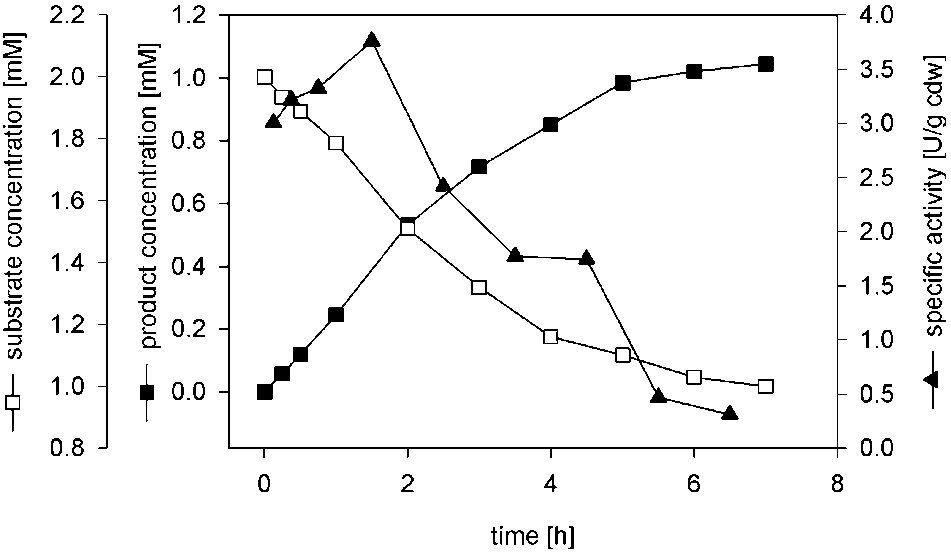
Biotransformation of cinnamonitrile using E. coli JM101 (pTEZ30) in shake flasks. Reaction was performed usingrestingcells (1.29 gcdw/L) in 20-mL shake flasks.
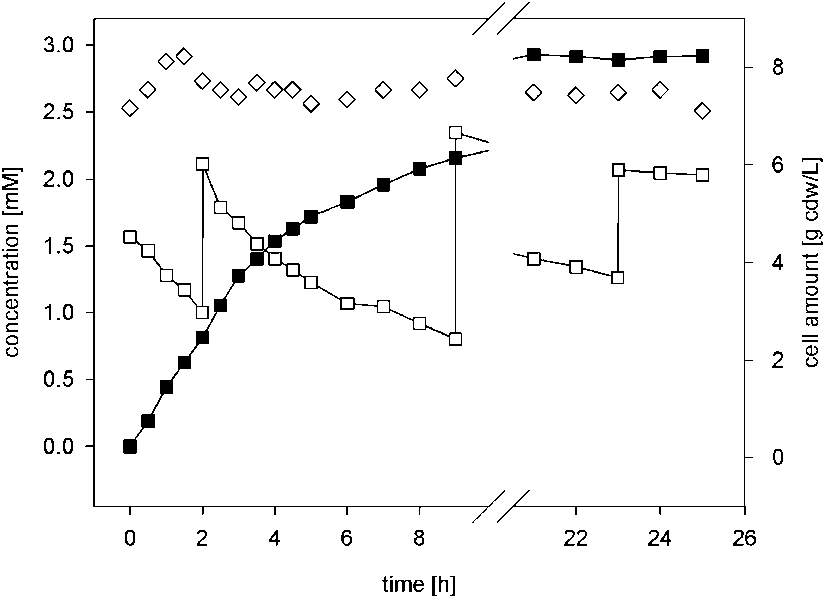
Biotransformation of cinnamonitrile using E. coli JM101 (pTEZ30) in a bioreactor on a 2-L scale.
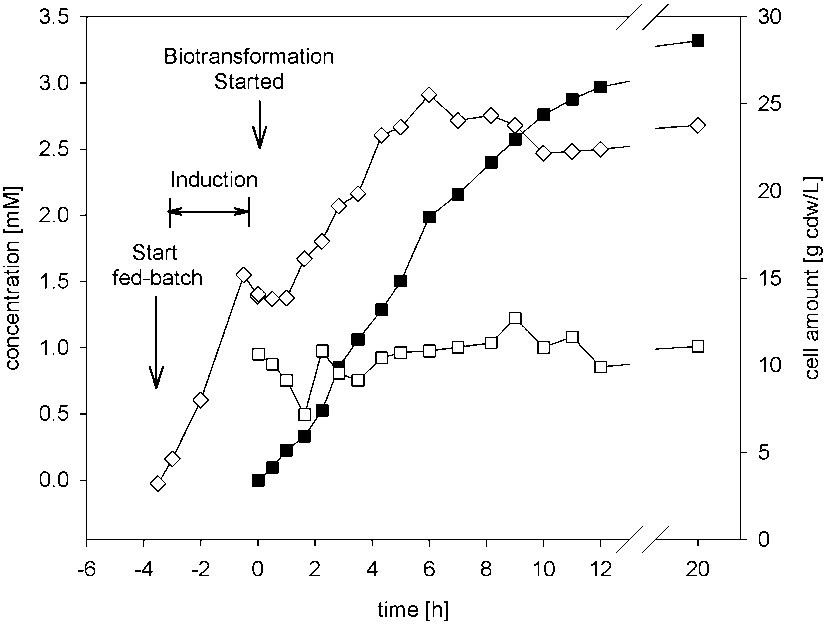
Biotransformation of cinnamonitrile using E. coli JM101 (pTEZ30) in a bioreactor with a 30-L workingvol-ume.
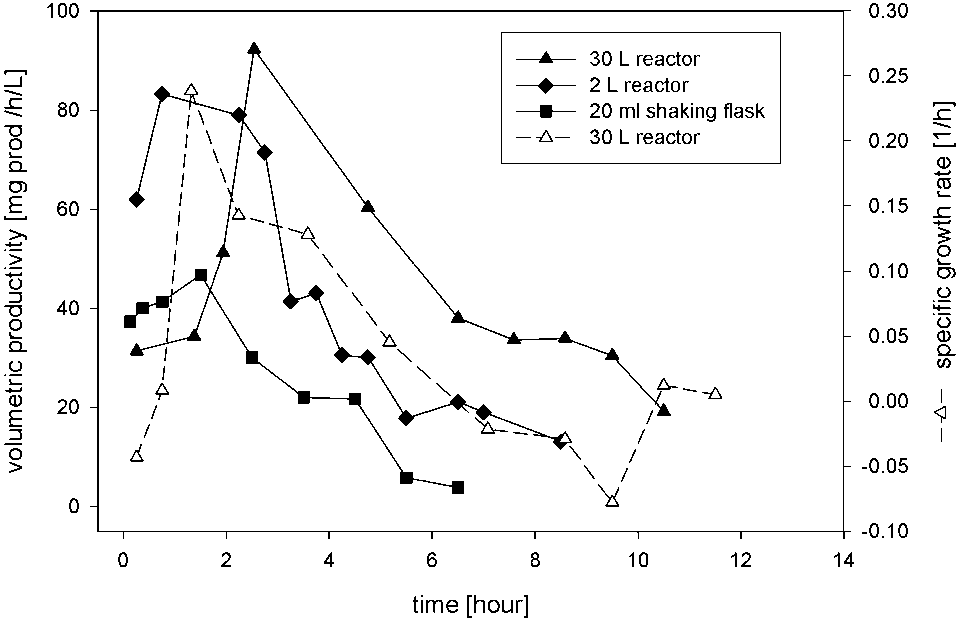
Volumetric productivities of biotransformation of cinnamonitrile using E. coli JM101 (pTEZ30) in shake-flasks, and in reactors on 2-L and 30-L scales, and the specific growth rate of the cells in a 30-L reactor.
Related Questions and Answers
No related questions yet