Bpc 157
CAS number: 137525-51-0
BPC-157 is a Protein drug with a maximum clinical trial phase of I.
Related images
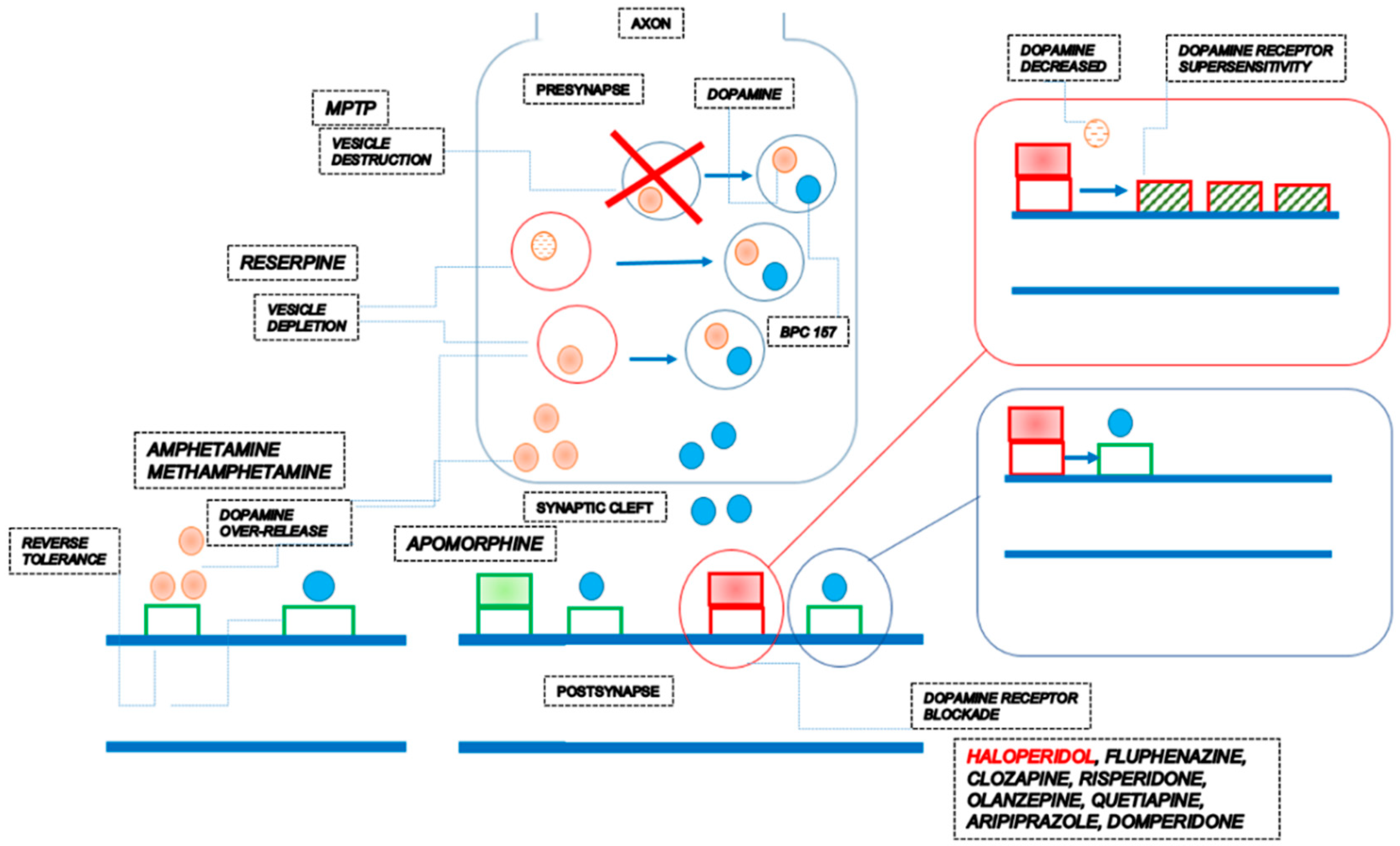
The stable gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157 pleiotropic beneficial activity and its possible relations with dopamine neurotransmitter activity assuming BPC 157 own presence in vesicles.
Related Questions and Answers
A: BPC 157 interacts significantly with the dopamine system to counteract various disturbances. It effectively counteracts issues caused by parkinsongenic neurotoxins like 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydrophyridine (MPTP) and vesicle depletion resulting from reserpine application. Additionally, BPC 157 antagonizes the effects of dopamine receptor blockades induced by agents such as haloperidol, fluphenazine, clozapine, and sulpiride, affecting both peripheral (e.g., gastric lesions, sphincter dysfunction, prolonged QTc intervals) and central (e.g., catalepsy, akinesia) manifestations. Furthermore, it counteracts disturbances, including stereotypies, in acute and chronic amphetamine applications (addressing both tolerance and reverse tolerance). It also antagonizes disturbances characteristic of amphetamine, methamphetamine, apomorphine, and dopamine over-stimulation in models simulating positive-like schizophrenia symptoms.
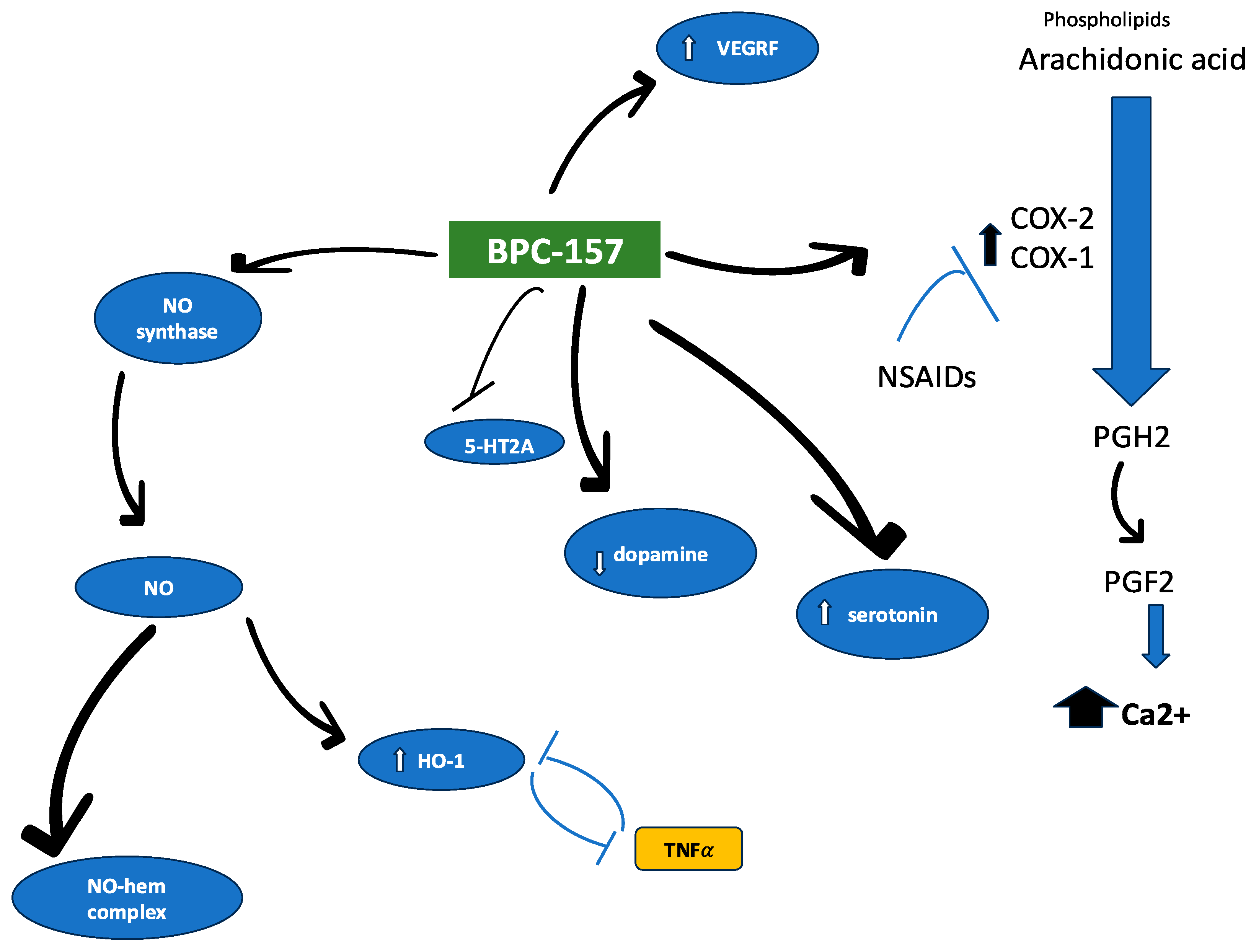
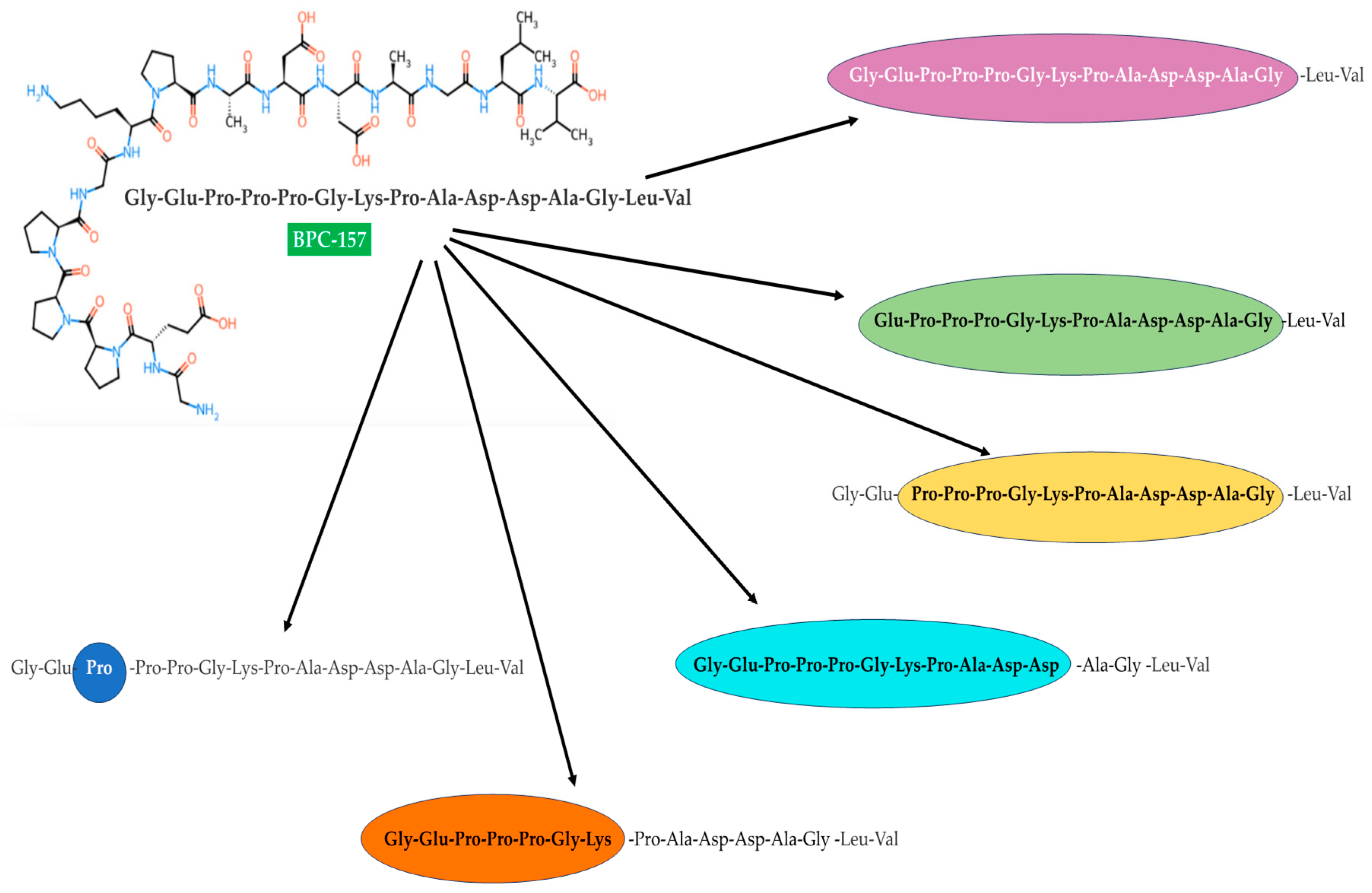
A: The amino acid sequence of BPC 157 is Gly-Glu-Pro-Pro-Pro-Gly-Lys-Pro-Ala-Asp-Asp-Ala-Gly-Leu-Val. Its molecular weight is 1419. BPC 157 possesses cytoprotective, anti-ulcer, and anti-inflammatory properties, which are linked to cell protection, the NO system, and cell migration.
A: BPC 157 is a peptide that has demonstrated anti-inflammatory, cytoprotective, and endothelial-protective effects in different organ systems and species. BPC 157's activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) is associated with nitric oxide (NO) release, tissue repair, and angiomodulatory properties. These actions can lead to improved vascular integrity and immune response, a reduced proinflammatory profile, and lower critical levels of the disease. As a result, its use as a potential prophylactic and complementary treatment for COVID-19 is considered critical.